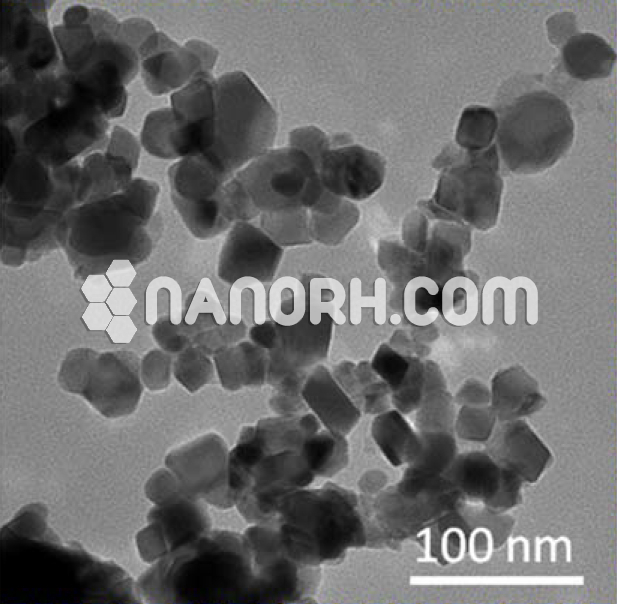
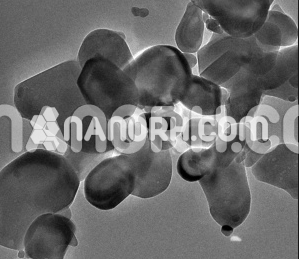
| Zirconium Tungstate Nanoparticles | |
| Product No | NRE-5277 |
| CAS No. | 16853-74-0 |
| Formula | Zr(WO4)2 |
| APS | <100nm (Can be Customized) |
| Purity | 99.9% |
| Color | White |
| Molecular Weight | 586.9g/mol |
| Density | 5.09g/cm3 |
| Melting Point | NA |
| Boiling Point | NA |
Zirconium Tungstate Nanoparticles
Applications:
Precision Instruments and Metrology
Thermal Management in Precision Instruments: The negative thermal expansion property of zirconium tungstate nanoparticles makes them ideal for precision instruments that require minimal changes in size with temperature fluctuations. These materials are used in optical instruments, telescopes, and other scientific devices where dimensional stability over a wide range of temperatures is critical.
Composite Materials for Electronics: ZrW₂O₈ nanoparticles are used in creating composite materials for high-precision electronics, where the material needs to maintain its shape and integrity despite temperature changes.
Thermal Barrier Coatings
Heat-Resistant Coatings: ZrW₂O₈ nanoparticles are used in thermal barrier coatings, especially in industries such as aerospace and automotive. These coatings help protect components from extreme temperatures, offering a combination of thermal stability and low thermal expansion that extends the lifespan of high-performance parts such as turbine blades and engine components.
Ceramic Coatings for High-Temperature Applications: Their ability to withstand high temperatures and maintain dimensional stability makes them valuable for coating materials exposed to high thermal stress.
Catalysis and Chemical Processing
Catalysts in Chemical Reactions: ZrW₂O₈ nanoparticles are used as catalysts or catalyst supports in a variety of chemical reactions, particularly in processes requiring high-temperature stability. Their unique properties also allow them to play a role in reactions that require specific thermal characteristics, such as those in petrochemical refining, hydrogen production, and industrial synthesis.
Environmental Catalysis: These nanoparticles can be used in applications aimed at reducing pollution, such as the catalytic reduction of nitrogen oxides (NOx) in vehicle exhausts or industrial emissions.
Energy Storage and Conversion
Fuel Cells: Zirconium tungstate nanoparticles have been explored for use in solid oxide fuel cells (SOFCs), which operate at high temperatures. Their thermal stability and conductivity make them a potential material for electrodes and electrolyte components in fuel cells, helping to improve the efficiency and longevity of energy conversion devices.
Supercapacitors: ZrW₂O₈ nanoparticles can also be used in energy storage devices, particularly supercapacitors, where their high surface area can enhance charge storage capabilities.