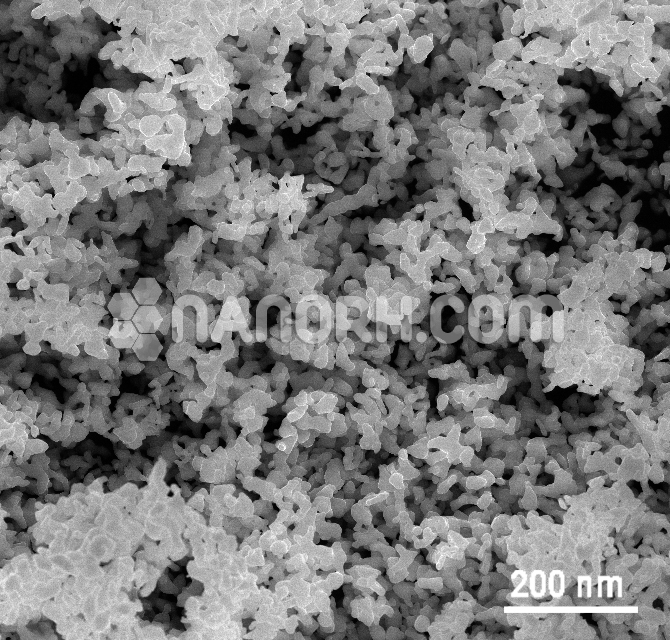
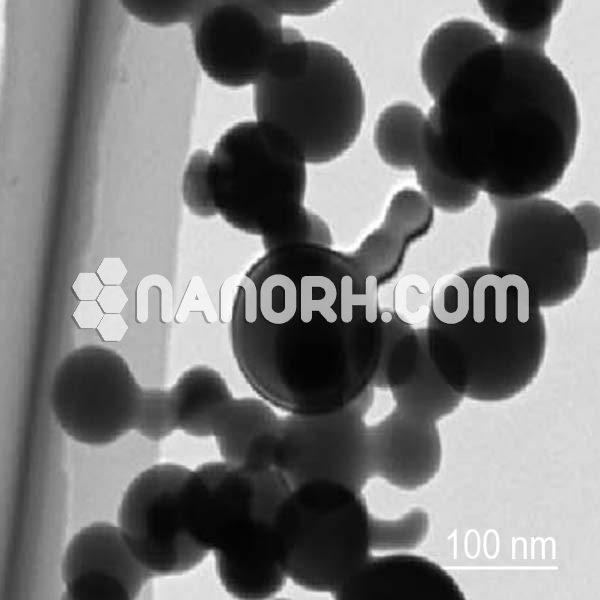
| Zirconium Sulfate Tetrahydrate Nanoparticles | |
| Product No | NRE-5276 |
| CAS No. | 7446-31-3 |
| Formula | Zr(SO4)2•4H2O |
| APS | <100 nm (Can be Customized) |
| Purity | 99.9% |
| Color | white |
| Molecular Weight | 355.396 g/mol |
| Density | 3.22 g/cm3 |
| Melting Point | 125° C |
| Boiling Point | NA |
Zirconium Sulfate Tetrahydrate Nanoparticles
Applications:
Catalysis and Chemical Processing
Catalysts for Organic Reactions: Zirconium sulfate nanoparticles are used as catalysts in various organic reactions such as esterification, oxidation, and polymerization. Their high surface area and reactivity enable them to accelerate chemical reactions efficiently, particularly in processes where acidic conditions are required.
Environmental Catalysis: These nanoparticles can also be used in catalytic processes to reduce pollutants and harmful emissions. For example, they can serve as a catalyst in the decomposition of harmful gases or in the reduction of sulfur compounds from industrial emissions.
Water Treatment and Environmental Applications
Water Softening and Filtration: Zirconium sulfate tetrahydrate nanoparticles are effective in water treatment processes, especially for the removal of heavy metals like lead, cadmium, and mercury from contaminated water. Their high reactivity allows them to adsorb heavy metals, making water purification more efficient.
Fluoride Removal: Zr(SO₄)₂·4H₂O nanoparticles are employed in the removal of fluoride ions from drinking water. Fluoride contamination in water can be harmful, and zirconium sulfate nanoparticles provide an effective solution by selectively adsorbing fluoride ions.
Wastewater Treatment: These nanoparticles can be used to remove various pollutants from wastewater, including dyes, organic compounds, and other hazardous substances, by acting as an adsorbent or catalyst in the treatment process.
Pharmaceutical and Biomedical Applications
Drug Delivery: The hydrophilic nature of zirconium sulfate tetrahydrate nanoparticles makes them a promising material for drug delivery applications. These nanoparticles can encapsulate drugs, enhancing their solubility, stability, and bioavailability. The nanoparticles can be designed to release the drugs in a controlled manner, improving therapeutic outcomes.
Biocompatibility: Zr(SO₄)₂·4H₂O nanoparticles are non-toxic and biocompatible, which makes them suitable for biomedical applications, particularly for use in drug delivery systems or as components in medical implants.