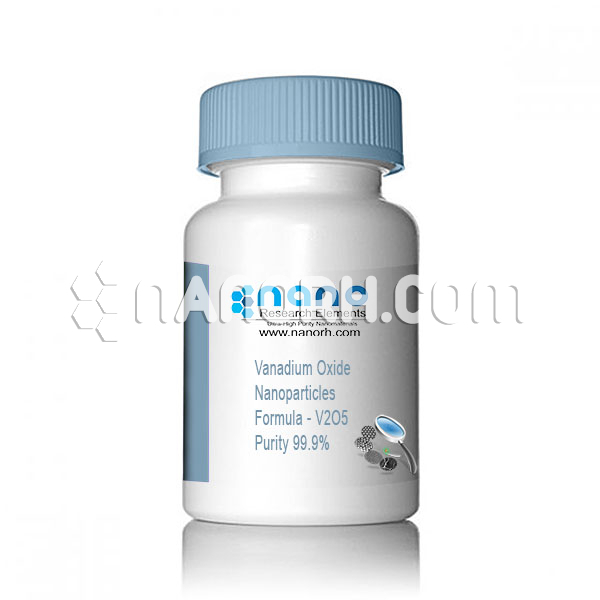
| Vanadium Oxide Nanoparticles | |
| Product Number | NRE-3063 |
| CAS No. | 1314-62-1 |
| Formula | V2O5 |
| Molecular Weight | 181.88 / g/mol |
| APS | <100 nm (Can be Customized) |
| Purity | 99.9% |
| Colour | Yellow |
| Density | 3.36 g/cm³ |
| Melting Point | 681 °C |
| Boiling Point | 1,750 °C |
Vanadium Oxide Nanoparticles
Vanadium oxide is widely used as a catalyst in many industrial chemical reactions. Vanadium oxide nanoparticles are black powder with a spherical surface. In optical applications such as laser crystal fabrication. in nanofibers and nanowires. In the manufacture of some alloys and ceramics.
Applications
Energy Storage:
Batteries: Vanadium oxide nanoparticles have significant potential in the field of energy storage, particularly in lithium-ion batteries and sodium-ion batteries. The material can be used as an anode or cathode material, improving the energy capacity, cycling stability, and charge/discharge efficiency. Vanadium oxide’s ability to undergo reversible redox reactions helps in enhancing battery performance.
Supercapacitors: In supercapacitors, V2O5 can be used to improve the energy density and power density of the device. Their high surface area and conductive properties help in storing charge more efficiently, leading to better performance in rapid charge/discharge cycles.
Vanadium Redox Flow Batteries: V₂O₅ nanoparticles are also being researched in vanadium redox flow batteries (VRFBs), which are a type of flow battery used for large-scale energy storage. The unique electrochemical properties of vanadium oxide contribute to the high efficiency and long life of these energy storage systems.
Catalysis:
Environmental Catalysis: Vanadium oxide nanoparticles are widely used as catalysts in environmental applications. For example, they are used in the reduction of nitrogen oxides (NOx) from industrial exhaust gases, particularly in selective catalytic reduction (SCR) systems, which are used to reduce air pollution from vehicles and industrial facilities.
Oxidation Reactions: V₂O₅ nanoparticles are highly effective in oxidation reactions, such as the conversion of alkenes to aldehydes and the oxidative dehydrogenation of hydrocarbons. Their ability to participate in redox reactions makes them valuable in the production of fine chemicals and in other industrial processes.
Degradation of Pollutants: Vanadium oxide nanoparticles can be used for the degradation of organic pollutants, such as dyes and pharmaceuticals, through photocatalysis. Under UV or visible light, V₂O₅ can activate oxygen molecules, breaking down harmful substances into less toxic compounds.