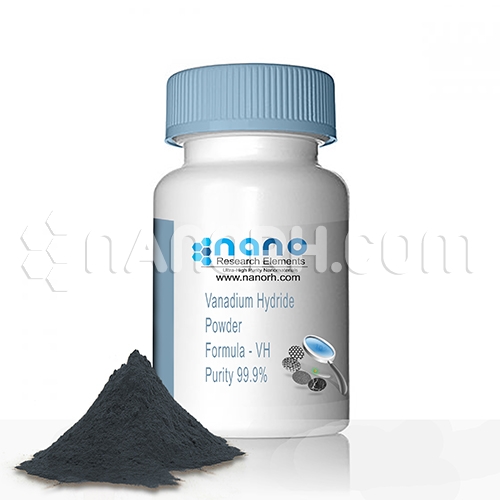
| Vanadium Hydride Nanoparticles | |
| Product No | NRE-5252 |
| CAS No. | 13966-93-3 |
| Formula | HV |
| Density | NA |
| APS | <100 nm (Can be Customized) |
| Purity | 99.9% |
| Form | Powder |
| Molecular Weight | 51.949 g/mol |
| Certificate Of Analysis | |
| V | 98.0% |
| H | 1.9% |
| C | 0.02% |
| Cr | 0.03% |
| Mg | 0.02% |
| S | 0.01% |
| B | 0.01% |
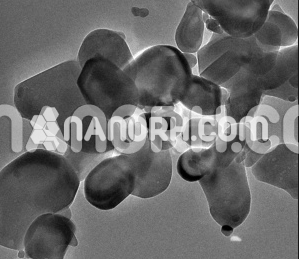
Vanadium Hydride Nanoparticles
Applications
Hydrogen Storage and Fuel Cells
Hydrogen Storage: Vanadium hydride nanoparticles are gaining attention for their ability to store hydrogen efficiently. Due to their high hydrogen absorption capacity, they are considered an ideal candidate for hydrogen storage systems, which are crucial for fuel cell technology, hydrogen-powered vehicles, and renewable energy storage.
Fuel Cells: These nanoparticles are used in hydrogen fuel cells, where they help in the reversible absorption and release of hydrogen. The use of VH nanoparticles in fuel cells improves the efficiency of hydrogen conversion into electrical energy, making them a key material for clean energy solutions.
Catalysis
Catalysts in Hydrogenation Reactions: Vanadium hydride nanoparticles are used as catalysts in hydrogenation reactions, which involve the addition of hydrogen to unsaturated compounds (such as in the production of pharmaceuticals, plastics, and petrochemicals). Their high surface area and ability to absorb hydrogen make them highly effective in facilitating these reactions.
Dehydrogenation Catalysts: Conversely, VH nanoparticles also serve as catalysts for dehydrogenation reactions, where hydrogen is removed from hydrocarbons. This application is important in oil refining, chemical production, and fuel processing.
Energy Storage and Supercapacitors
Supercapacitors: Due to their high surface area and hydrogen storage capacity, vanadium hydride nanoparticles are explored for use in supercapacitors. These energy storage devices are critical for applications requiring rapid charge/discharge cycles and high power densities, such as in electric vehicles and renewable energy systems.
Batteries: VH nanoparticles are also studied for use in lithium-ion batteries and sodium-ion batteries. The high hydrogen absorption and release capabilities can enhance the performance of battery electrodes, leading to better charge retention and cycle life.