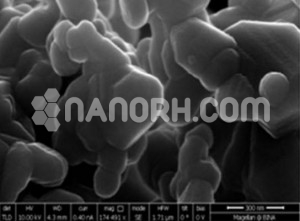
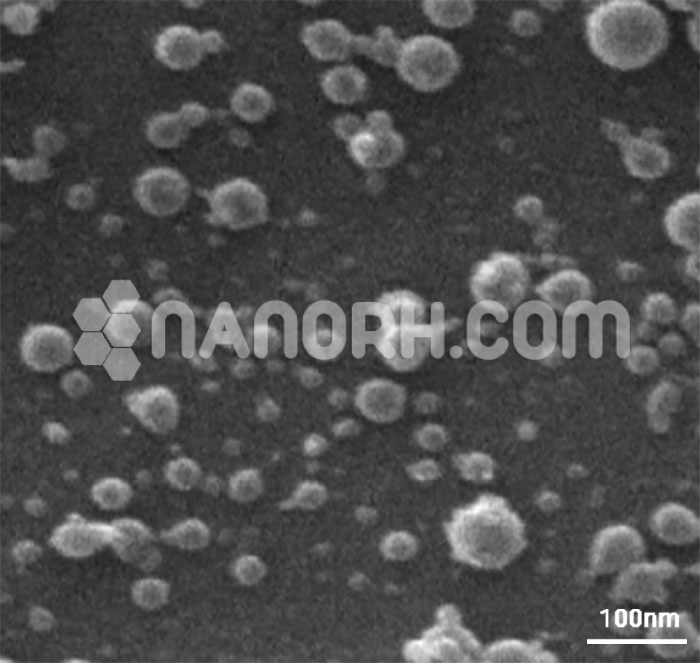
| Strontium Dodecairon Nonadecaoxide Nanopowder | |
| Product No | NRE-29039 |
| CAS No. | 12023-91-5 |
| Formula | SrFe12O19 |
| APS | <200nm (Can be Customized) |
| Purity | 99.8% |
| Color | Black |
| Molecular Weight | 1061.77 g/mol |
| Density | 4.7-5.0 gm/cc at 0°C |
| Melting Point | 450 °C |
| Boiling Point | NA |
Strontium Dodecairon Nonadecaoxide Nanopowder
Strontium Dodecairon Nonadecaoxide Nanopowder (Sr₁₂Fe₁₉O₁₉), commonly referred to as strontium ferrite, is a complex, high-performance ceramic material composed of strontium (Sr), iron (Fe), and oxygen (O) atoms. This nanopowder is part of the family of ferrites and is characterized by its unique crystalline structure and magnetic properties, making it an important material for various advanced applications.
Strontium ferrite compounds have a hexagonal or rhombohedral crystal structure, which is formed by the combination of strontium ions and iron oxide in specific proportions. The most notable feature of strontium ferrite is its magnetic behavior, as it exhibits high coercivity and remanence, which are essential for use in permanent magnets and magnetic applications. The nanopowder form of this material presents several advantages over bulk materials, particularly in applications where surface area and particle size play a crucial role in enhancing the material’s properties and performance.
In its nanopowder form, Sr₁₂Fe₁₉O₁₉ has enhanced characteristics, including a larger surface area-to-volume ratio, improved reactivity, and increased performance in magnetic devices. The reduced particle size of the powder enhances its ability to be incorporated into various substrates and composite materials, leading to a broader range of functional uses. These attributes make it a suitable candidate for a wide array of industrial, technological, and medical applications, especially where high magnetic properties and stability are required.
The preparation of strontium dodecairon nonadecaoxide nanopowder typically involves high-energy methods such as sol-gel processing, co-precipitation, or hydrothermal synthesis. These methods ensure that the powder has a consistent size distribution, high crystallinity, and purity, all of which contribute to its superior performance.