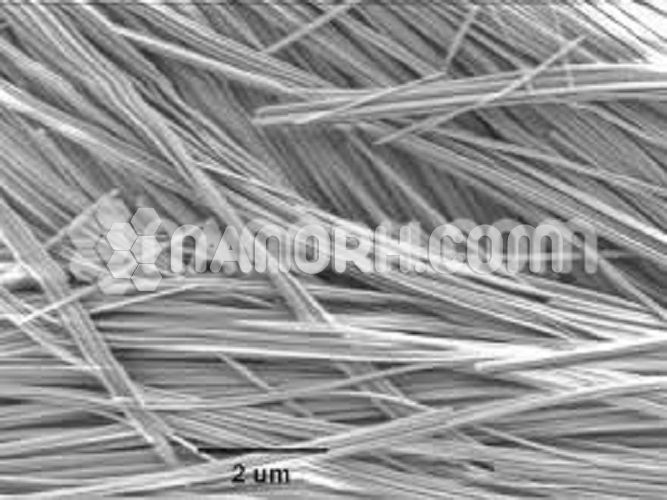
Sodium Ammonium Trimolybdate Nanowires
Sodium Ammonium Trimolybdate Nanowires are novel alkali metal-ceramic nanomaterials for dye degradation from textile wastewater, catalysis, and other high technology research applications. Please request a quote above to receive pricing information based on your desired quantity.
| Sodium Ammonium Trimolybdate Nanowires | |
| Product No | NRE-13011 |
| CAS No. | 7440-22-4 |
| Formula | NaNH4Mo3O10 |
| Average diameter | 150-200nm |
| Average Length | up to 15um |
| Purity | 99.9% |
| Molecular Weight | 488.84 g/mol |
| Density | NA |
| Melting Point | NA |
| Boiling Point | NA |
Sodium Ammonium Trimolybdate Nanowires are novel alkali metal-ceramic nanomaterials for dye degradation from textile wastewater, catalysis, and other high technology research applications. Please request a quote above to receive pricing information based on your desired quantity.
Photocatalysis:
Water Splitting for Hydrogen Production: The semiconducting properties of sodium ammonium trimolybdate nanowires allow them to absorb light and generate electron-hole pairs, which can catalyze the splitting of water molecules to produce hydrogen. This makes them potential materials for photocatalytic water splitting and renewable hydrogen production, a key process in sustainable energy solutions.
Pollutant Degradation: Sodium ammonium trimolybdate nanowires can be employed in photocatalysis for the degradation of organic pollutants, such as dyes and pesticides, under UV or visible light irradiation. This is beneficial in wastewater treatment and environmental cleanup applications.
Nanocomposites and Coatings:
Nanocomposite Materials: These nanowires can be incorporated into various matrices to create nanocomposites with enhanced mechanical, electrical, and thermal properties. They can improve the performance of polymers, ceramics, and metals used in structural materials, electronic devices, or protective coatings.
Coatings for Corrosion Resistance: The molybdenum oxide framework in provides excellent resistance to corrosion, making them suitable for use in protective coatings for metal surfaces exposed to harsh environments, such as in marine or aerospace applications.
Photonic and Optoelectronic Devices:
Optical Modulators: The optical properties of can be leveraged in photonics, such as in optical modulators and light-emitting devices. Their ability to interact with light could enable their use in optical communication systems or display technologies.
Light-Emitting Diodes (LEDs): The photonic properties of these nanowires may also be utilized in the development of LEDs or laser devices, where they can help improve the efficiency and brightness of light emissions.
Biological and Biomedical Applications:
Drug Delivery: Sodium ammonium trimolybdate nanowires may also have potential in drug delivery systems. Their high surface area allows for efficient drug loading, and their biocompatibility makes them attractive candidates for targeted delivery of therapeutic agents.
Antibacterial and Antifungal Activity: Some studies suggest that molybdenum-based materials exhibit antimicrobial properties, making sodium ammonium trimolybdate nanowires potentially useful in biomedical applications, such as in wound healing, medical devices, and antibacterial coatings.