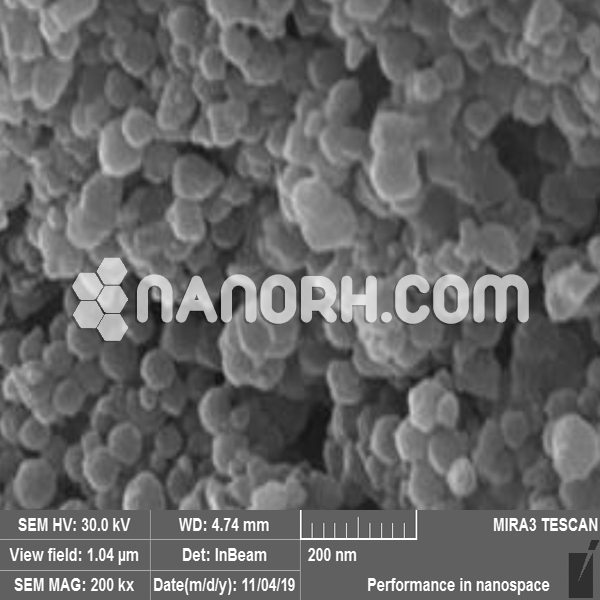
| Saponite Clay Nanoparticles | |
| Product No | NRE-6028 |
| CAS No. | 1319-41-1 |
| Formula | NA |
| APS | <80nm (Can be Customized) |
| Purity | 99% |
| Color | White/yellow/greenish |
| Molecular Weight | 480.19 g/mol |
| Density | 2.3 g/cm3 |
| Melting Point | NA |
| Boiling Point | NA |
Saponite Clay Nanoparticles
Applications
The unique properties of Saponite Clay Nanoparticles make them highly suitable for a wide range of applications in several industries:
Environmental Remediation
Pollutant Removal:
Saponite nanoparticles are effective in removing pollutants from air, water, and soil due to their high adsorption and ion-exchange properties. They can absorb heavy metals, organic pollutants, and even oil spills in contaminated environments.
Water Purification:
Their high cation-exchange capacity (CEC) allows saponite nanoparticles to be used in water treatment processes, where they can remove toxic metals and other contaminants from industrial wastewater.
Drug Delivery Systems
Nano-Drug Carriers:
The intercalated structure of saponite clay allows it to be used as a drug delivery system. The nanoparticles can be loaded with medications and released in a controlled manner, making them suitable for targeted drug delivery in the treatment of diseases.
Biocompatibility:
Saponite’s natural origin and biodegradability make it a safe material for use in biomedical applications, including wound healing and gene delivery.
Agriculture and Soil Improvement
Soil Conditioners:
Saponite nanoparticles can be used as soil conditioners to improve soil structure, moisture retention, and nutrient exchange. They help enhance soil fertility, especially in arid or nutrient-poor regions.
Pesticide Delivery:
Due to their ability to intercalate molecules, saponite nanoparticles can be used for the controlled release of fertilizers or pesticides, allowing for more efficient agricultural practices.
Polymer Nanocomposites
Reinforcement in Polymers:
Saponite nanoparticles can be incorporated into polymers to enhance their mechanical, thermal, and barrier properties. These nanocomposites are used in the production of lightweight materials, coatings, and films with improved strength and durability.
Nanoclay-Polymer Composites:
Saponite can be combined with various polymers to create high-performance materials used in automotive parts, packaging, and construction materials.
Catalysis and Chemical Processes
Green Catalysis:
The catalytic properties of saponite nanoparticles allow them to be used in environmentally friendly chemical reactions, such as those in green chemistry. They are particularly useful in organic synthesis, petrochemical processing, and biodegradable polymer production.
Reaction Enhancement:
Saponite nanoparticles can serve as solid catalysts in reactions such as hydrocarbons cracking, dehydrogenation, and oxidation, offering an alternative to more hazardous traditional catalysts.