| Rubidium Tungstate Nanoparticles | |
| Product No | NRE-5191 |
| CAS No. | 13597-52-9 |
| Formula | Rb2WO4 |
| APS | <100nm (Can be Customized) |
| Purity | 99.9% |
| Color | Colorless |
| Molecular Weight | 418.77g/mol |
| Density | 3.51 g/cm3 |
| Melting Point | NA |
| Boiling Point | NA |
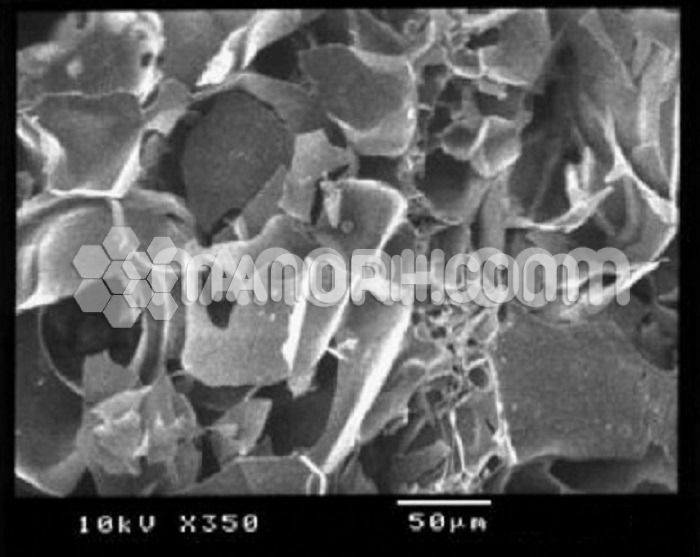
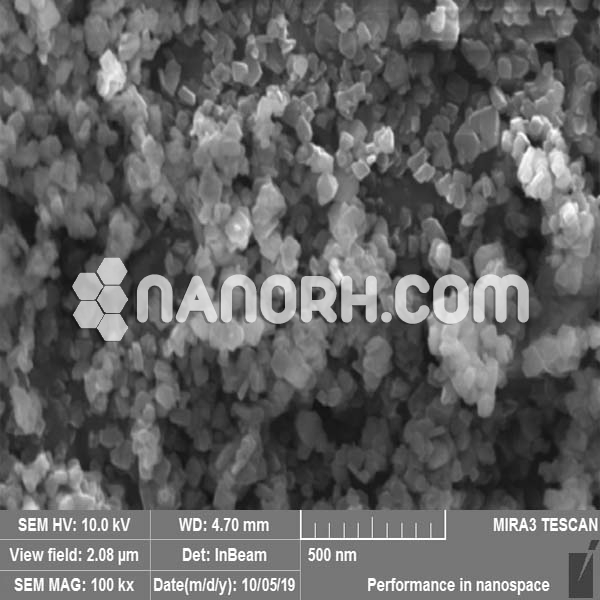
Rubidium Tungstate Nanopaticles
Applications
Catalysis
Catalysis in Chemical Reactions: Rubidium tungstate nanoparticles can be used as catalysts or as catalyst supports in various chemical processes. Their high surface area and reactivity enhance their ability to accelerate reactions, particularly in organic synthesis, hydrogenation, and oxidation reactions.
Environmental Catalysis: can also be used for environmental applications, such as the degradation of pollutants or harmful chemicals in water and air. Their catalytic properties make them suitable for waste treatment processes.
Energy Storage and Conversion
Supercapacitors: Due to their excellent electrical conductivity and high surface area, rubidium tungstate nanoparticles are promising materials for use in supercapacitors. Supercapacitors require efficient charge storage and rapid charge/discharge cycles, and rubidium tungstate can help improve the performance of these energy storage devices.
Battery Technology: Rubidium tungstate nanoparticles may also be used in rechargeable batteries. Their ability to conduct electricity and their stability at various temperatures can improve the performance of lithium-ion or sodium-ion batteries, enhancing their capacity and lifespan.
Photovoltaic Devices: Rubidium tungstate nanoparticles have potential applications in solar cells. Their interaction with light and electrical conductivity can contribute to the efficiency of energy conversion in solar technologies.
Optical and Photonic Applications
Optoelectronic Devices: Rubidium tungstate nanoparticles can be used in optoelectronic devices such as light-emitting diodes (LEDs), photodetectors, and lasers. Their ability to interact with light makes them useful in the design of devices that require precise control over light emission and absorption.
Nonlinear Optical Materials: Due to their unique electronic properties, can be used in nonlinear optical applications, such as frequency doubling or light modulation, which are essential in telecommunications and advanced optical systems.