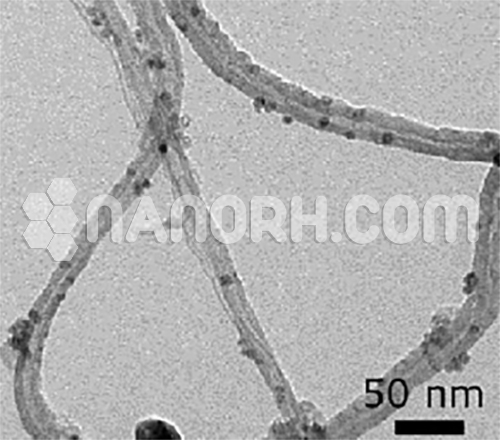
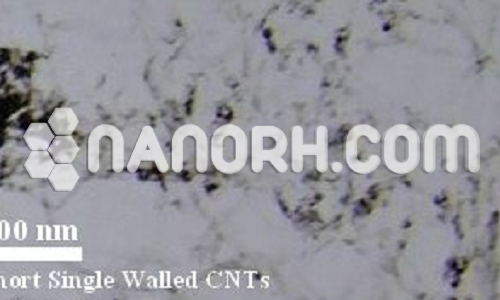
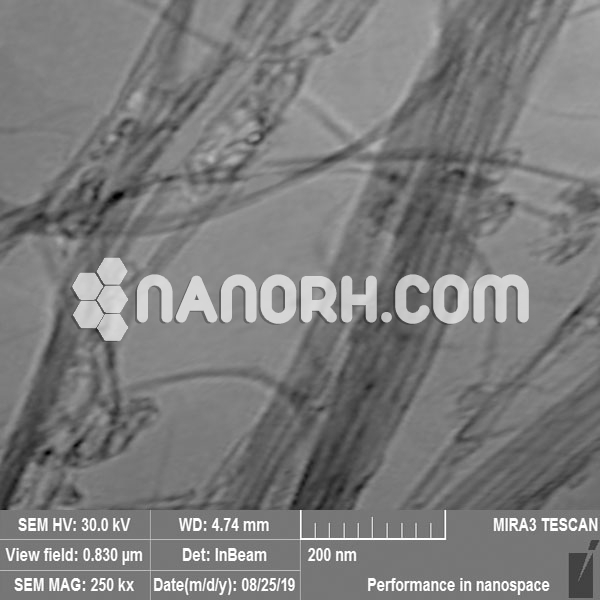
Platinum coated Carbon Nanotubes (Pt/CNT)
| Platinum coated Carbon Nanotubes | |
| Product No | NRE-42006 |
| CAS No. | 7440-06-4/308068-56-6 |
| Outer Diameter | 35-50 nm |
| Inner Diameter | 5-25nm |
| Average Length | 10-20um |
| True Density | 2.1 g/cm3 |
| Electric Conductivity | > 100 S/cm |
| Metal Percentage | 2-5% (can be Customized) |
Platinum coated Carbon Nanotubes – exhibit outstanding chemical activity due to their large active surface area and unique crystallographic surface structure.
CNTs decorated with metal nanoparticles (NPs) like Silver nanoparticles, Gold nanoparticles, Nickel nanoparticles, copper nanoparticles, Magnesium nanoparticles, palladium nanoparticles, platinum nanoparticles, exhibit outstanding chemical activity due to their large active surface area and unique crystallographic surface structure.
Applications
Catalysis and Chemical Reactions
Hydrogenation and Dehydrogenation: Platinum is one of the most effective catalysts for hydrogenation (the addition of hydrogen to molecules, such as unsaturated hydrocarbons) and dehydrogenation (the removal of hydrogen). Pt-CNTs significantly enhance the efficiency of these reactions due to the high surface area of CNTs, which provides more active sites for platinum to interact with the reactants.
Fuel Cells: Platinum is the catalyst of choice for both the hydrogen oxidation reaction (HOR) and oxygen reduction reaction (ORR) in proton exchange membrane fuel cells (PEMFCs). Pt-CNTs are used as electrodes in fuel cells, where their high catalytic activity, stability, and conductivity improve fuel cell performance, especially in terms of energy efficiency and longevity.
Catalysis in Industrial Reactions: Pt-CNTs are used in a variety of industrial processes, such as refining, pharmaceutical manufacturing, and the production of specialty chemicals. Platinum’s ability to catalyze reactions without being consumed makes Pt-CNTs highly valuable for large-scale chemical manufacturing, such as in petroleum refining or in the production of fine chemicals.
Energy Storage and Conversion
Hydrogen Storage: Platinum-coated CNTs are being investigated for use in hydrogen storage applications. Platinum can absorb hydrogen, and when it is deposited on CNTs, the composite can store hydrogen efficiently. This is important for applications in hydrogen-powered fuel cells and for creating compact, efficient hydrogen storage systems.
Supercapacitors and Batteries: Pt-CNTs can be utilized in energy storage devices such as supercapacitors and batteries. The combination of platinum’s conductivity and the high surface area of CNTs enhances the energy storage and release capabilities of these devices, which are critical for applications in electric vehicles, portable electronics, and renewable energy systems.
Fuel Cells: Beyond hydrogen fuel cells, Pt-CNTs have been explored for other types of fuel cells, such as direct methanol fuel cells (DMFCs), where platinum is used to catalyze the oxidation of methanol to generate electricity.