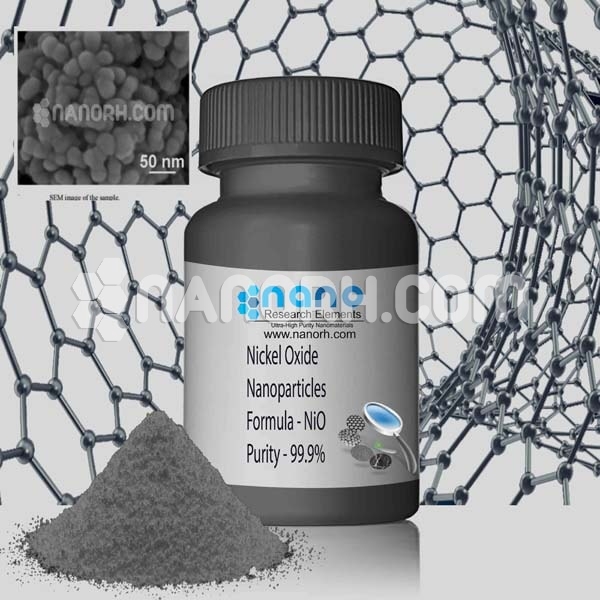
| Nickel Oxide Nanoparticles | |
| Product No | NRE-29032 |
| CAS No. | 1313-99-1 |
| Formula | NiO |
| APS | <100nm (Can be Customized) |
| Purity | 99.9% |
| Color | Black |
| Molecular Weight | 74.692 g/mol |
| Density | 6.67 g/cm³ |
| Melting Point | 1955 °C |
| Boiling Point | NA |
Nickel Oxide Nanoparticles
Nickel oxide nanoparticles are a type of inorganic compound made from nickel and oxygen, typically in the form of a black or greenish-black solid. They belong to the class of metal oxides and are known for their unique electronic, magnetic, and catalytic properties, which make them attractive for a wide range of applications. NiO nanoparticles are usually produced via methods like sol-gel, co-precipitation, hydrothermal synthesis, and chemical vapor deposition, where the controlled particle size, morphology, and surface area significantly influence their properties.
Properties
High Surface Area: The small size of NiO nanoparticles increases their surface area, enhancing their catalytic activity and making them suitable for various electrochemical applications.
Magnetic Properties: NiO nanoparticles are antiferromagnetic at room temperature, meaning their magnetic moments align in opposite directions within the material. However, when modified or doped with other elements, their magnetic properties can be tuned for specific applications.
Electrical Conductivity: NiO is generally an insulator or semiconductor, but doping or nanostructuring can make it more conductive, particularly useful in electronic and energy storage devices.
Chemical Stability: NiO nanoparticles exhibit good chemical stability, which is important for their durability in various applications, especially in catalysis and energy-related processes.
Applications
Catalysis:
Environmental Catalysis: NiO nanoparticles are widely used in the catalytic oxidation of organic compounds, including in the removal of pollutants from exhaust gases or industrial emissions. They can act as catalysts in reactions that degrade harmful substances, such as CO, NOx, and volatile organic compounds (VOCs), into less harmful products.
Fuel Cells: NiO nanoparticles are used as catalysts in the development of fuel cells, particularly in processes like the oxidation of hydrogen or alcohols. They help in improving the efficiency and stability of the fuel cells, which are important for clean energy technologies.
Water Splitting: NiO is studied for its role in the electrochemical splitting of water to produce hydrogen, a clean fuel. NiO nanoparticles, especially when doped or combined with other materials, show potential as catalysts in this important process for sustainable energy production.
Energy Storage:
Supercapacitors: NiO nanoparticles are used in supercapacitors, where their high surface area and electrical conductivity help store energy efficiently. NiO-based supercapacitors offer high energy density and long cycle life, making them suitable for applications in power backup, electric vehicles, and renewable energy storage.