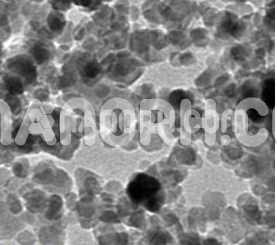
| Neodymium Iron Boron Nanoparticles | |
| Product No | NRE-5282 |
| CAS No. | 918106-59-9 |
| Formula | NdFeB |
| APS | <100nm (Can be Customized) |
| Purity | 99.9% |
| Color | Silver Grey |
| Molecular Weight | 210.896 g/mol |
| Density | 7.5 g/cm³ |
| Melting Point | NA |
| Boiling Point | NA |
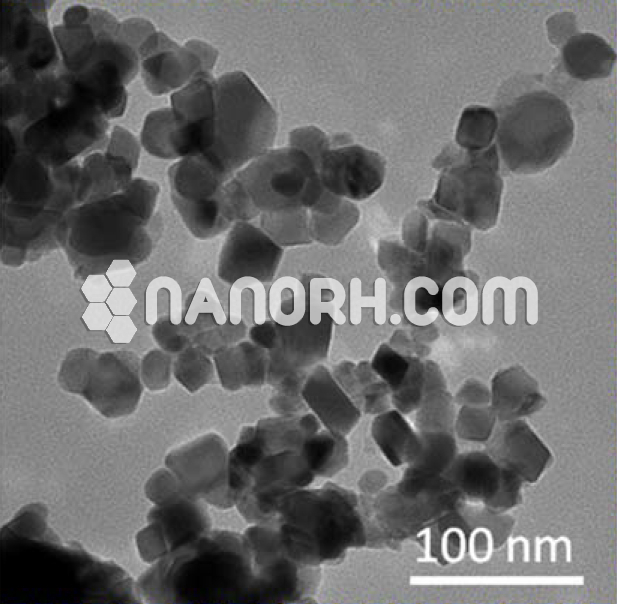
Neodymium Iron Boron Nanoparticles
Neodymium-Iron-Boron (NdFeB) nanoparticles are high-performance magnetic materials composed of an alloy of neodymium (Nd), iron (Fe), and boron (B). This alloy, widely known for its exceptional magnetic properties, is the basis for the production of permanent magnets with high magnetic strength. Neodymium, a rare-earth metal, significantly enhances the magnetic properties of the alloy, while iron and boron contribute to its structure, stability, and cost-effectiveness.
Neodymium (Nd): A rare-earth element, neodymium is crucial in enhancing the magnetic properties of the alloy. It increases the magnetization of the material and improves the overall strength of the magnet.
Iron (Fe): Iron is a ferromagnetic material that provides the magnetic framework for the NdFeB alloy. It plays a crucial role in defining the magnet’s performance and durability.
Boron (B): Boron acts as a stabilizing element in the NdFeB alloy. It strengthens the bond between the neodymium and iron atoms, improving the material’s resistance to corrosion and enhancing its overall structural integrity.
Synthesis
The synthesis of NdFeB nanoparticles typically involves several methods that allow control over particle size, morphology, and composition. Common techniques include:
Ball Milling: High-energy ball milling is a widely used technique to produce NdFeB nanoparticles. The process involves grinding neodymium, iron, and boron powders together, which results in the formation of fine particles with a uniform alloy structure.
Chemical Reduction: This method involves the reduction of neodymium and iron salts in the presence of boron to form NdFeB nanoparticles. It allows precise control over the composition and size of the nanoparticles.
Sol-Gel Process: The sol-gel technique is used to create a uniform mixture of neodymium, iron, and boron precursors in solution, followed by gelation and heat treatment to produce the nanoparticles.
Hydrothermal Synthesis: A hydrothermal process can be employed to synthesize NdFeB nanoparticles by reacting neodymium, iron, and boron in a high-temperature aqueous solution. This method provides high-purity nanoparticles with a controlled morphology.