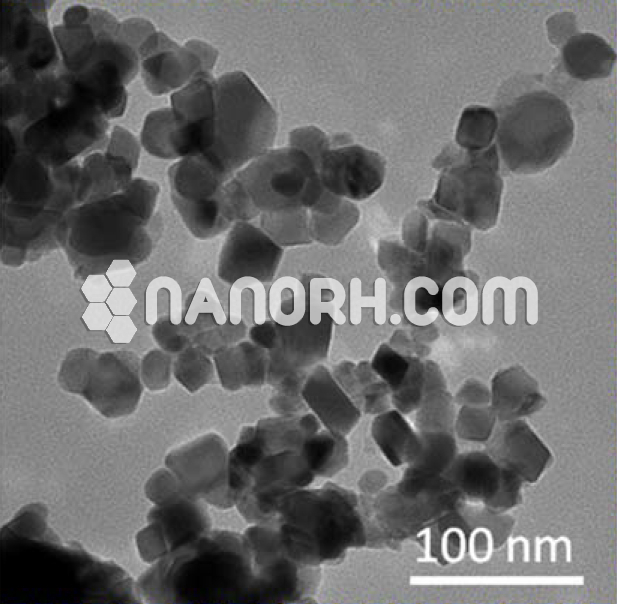
| Manganese Oxide Nanopowder | |
| Product No | NRE-3039 |
| CAS No. | 1317-34-6 |
| Formula | Mn2O3 |
| APS | <100nm (Can be Customized) |
| Purity | 99.9% |
| Color | Dark Brown |
| Molecular Weight | 157.87 g/mol |
| Density | 4.5 g/cm³ |
| Melting Point | 888°C |
| Boiling Point | NA |
Manganese Oxide Nanopowder Applications:
Applications:
Energy Storage and Conversion
Lithium-Ion Batteries (LIBs): Manganese oxide nanopowder is used as a cathode material in lithium-ion batteries (LIBs). It improves the energy storage capacity, cycling stability, and performance of batteries, making them ideal for applications in electric vehicles, portable electronics, and renewable energy storage.
Supercapacitors: The high surface area and fast charge/discharge characteristics of MnOₓ nanopowder make it an excellent material for supercapacitors, which are energy storage devices used in applications requiring rapid bursts of energy, such as electric vehicles, wind energy systems, and grid storage.
Fuel Cells: Manganese oxide nanopowder is used as an electrocatalyst in fuel cells, particularly for oxygen reduction reactions (ORR). This improves the performance of hydrogen fuel cells and direct methanol fuel cells, offering a low-cost alternative to precious metal catalysts like platinum.
Catalysis
Environmental Catalysis: Manganese oxide nanopowder is widely used in the catalytic conversion of volatile organic compounds (VOCs) and nitrogen oxides (NOx). This makes MnOₓ nanopowder an important material for air purification systems and automotive catalytic converters to reduce harmful emissions.
Water Treatment: MnOₓ nanopowder is effective in water purification due to its ability to adsorb and remove heavy metals (such as arsenic, lead, and cadmium) and organic pollutants from contaminated water. It is also used in advanced oxidation processes (AOPs) to degrade pollutants.
Organic Synthesis: Manganese oxide nanopowder serves as a catalyst for a variety of oxidation reactions in organic synthesis, including the oxidation of alcohols, aldehydes, and other compounds, which are useful for the production of fine chemicals and pharmaceuticals.