| Magnesium Fluoride Nanoparticles | |
| Product No | NRE-5144 |
| CAS No. | 7783-40-6 |
| Formula | MgF2 |
| APS | <100nm (Can be Customized) |
| Purity | 99.9% |
| Color | White |
| Molecular Weight | 62.301 g/mol |
| Density | 3.148 g/cm³ |
| Melting Point | 1263°C |
| Boiling Point | 2260 °C |
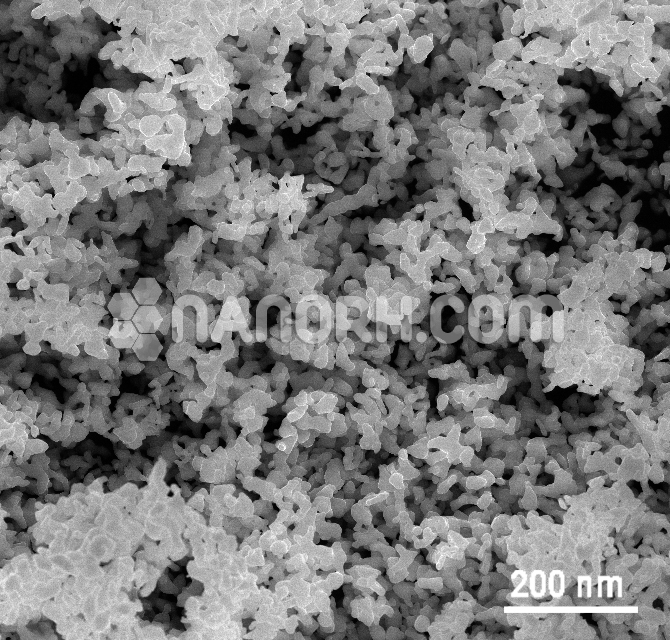
Magnesium Fluoride Nanoparticles / Nanopowder
Introduction
Magnesium Fluoride (MgF₂) is an inorganic compound consisting of magnesium and fluorine. When synthesized as nanoparticles or nanostructures (nanopowder), MgF₂ exhibits unique properties compared to its bulk form. These properties include:
Increased Surface Area: Nanoparticles have a much larger surface area-to-volume ratio compared to bulk materials. This can lead to enhanced reactivity and improved performance in various applications.
Optical Properties: MgF₂ nanoparticles are known for their excellent transparency in the ultraviolet (UV) and visible regions of the electromagnetic spectrum, making them highly suitable for optical applications.
Synthesis
Magnesium fluoride nanoparticles are typically synthesized through methods such as:
Sol-Gel Method: A precursor solution is used to form a gel, followed by heat treatment to produce nanoparticles. This method is commonly used for creating MgF₂ with high purity and uniform particle size.
Hydrothermal Synthesis: This method involves a high-pressure reaction in water at elevated temperatures, leading to the formation of well-defined nanoparticles.
Applications
Optical and Photonic Devices:
Lenses and Coatings: MgF₂ is used in optical coatings, particularly in UV and infrared optics, for anti-reflection coatings, lenses, and mirrors. Its high transparency in the UV range makes it ideal for lasers and imaging systems.
UV Filters: Due to its strong UV transparency and low absorption, MgF₂ nanoparticles are utilized in UV filters and optical windows for photonics and microscopy.
Electronics:
High-Temperature Insulators: MgF₂ nanoparticles are used as insulators in high-temperature environments, including electronics and semiconductor devices, because of their stability and electrical insulating properties.
Dielectric Materials: In capacitors and other electronic components, MgF₂ nanostructures are utilized for their dielectric properties.