| Lead Nitrate Nanoparticles | |
| Product No | NRE-5127 |
| CAS No. | 10099-74-8 |
| Formula | (Pb(NO3)2 |
| APS | <100nm (Can be Customized) |
| Purity | 99.9% |
| Color | White |
| Molecular Weight | 331.21g/mol |
| Density | 4.53g/cm³ |
| Melting Point | 470°C |
| Boiling Point | NA |
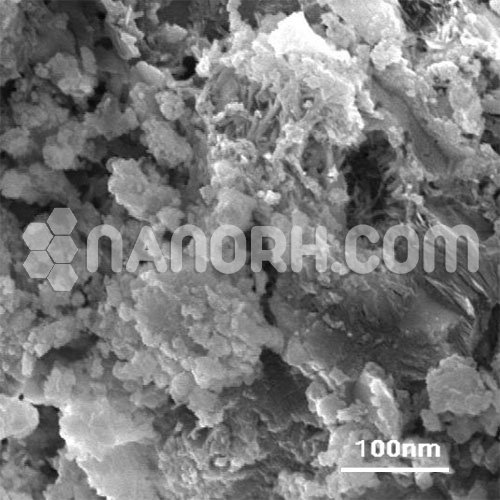
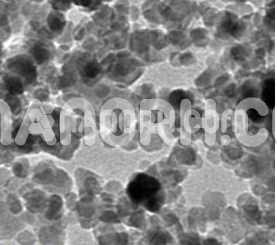
Lead Nitrate Nanoparticles
Introduction
Lead nitrate (Pb(NO₃)₂) is an inorganic compound consisting of lead (Pb²⁺) and nitrate ions (NO₃⁻). It appears as a white, crystalline solid and is highly soluble in water. Pb(NO₃)₂ is commonly used in chemical synthesis, laboratory reactions, and as a precursor for the production of other lead compounds.
Properties
Increased Reactivity:
Due to their high surface-to-volume ratio, Pb(NO₃)₂ nanoparticles exhibit enhanced reactivity compared to bulk lead nitrate. This makes them effective in chemical reactions, catalysis, and photochemical processes.
Solubility:
Pb(NO₃)₂ is highly soluble in water, and the nanoparticles retain this property, making them useful in applications that require high dissolution rates or interactions in aqueous environments.
Quantum Effects:
Like many other nanoparticles, Pb(NO₃)₂ nanoparticles can exhibit quantum confinement effects, where the electronic properties of the material change due to the nanoscale size. These effects can lead to altered optical properties (such as changes in absorption and emission spectra) compared to bulk Pb(NO₃)₂.
Electrochemical Properties:
Pb(NO₃)₂ nanoparticles can exhibit interesting electrochemical behaviors, making them potential candidates for use in energy storage and battery technologies, where high surface area and efficient charge transfer are critical.
Toxicity and Environmental Concerns:
As with most lead-based compounds, lead nitrate nanoparticles are toxic, posing risks to both human health and the environment. Exposure can lead to lead poisoning, and care must be taken when handling or disposing of Pb(NO₃)₂ nanoparticles.