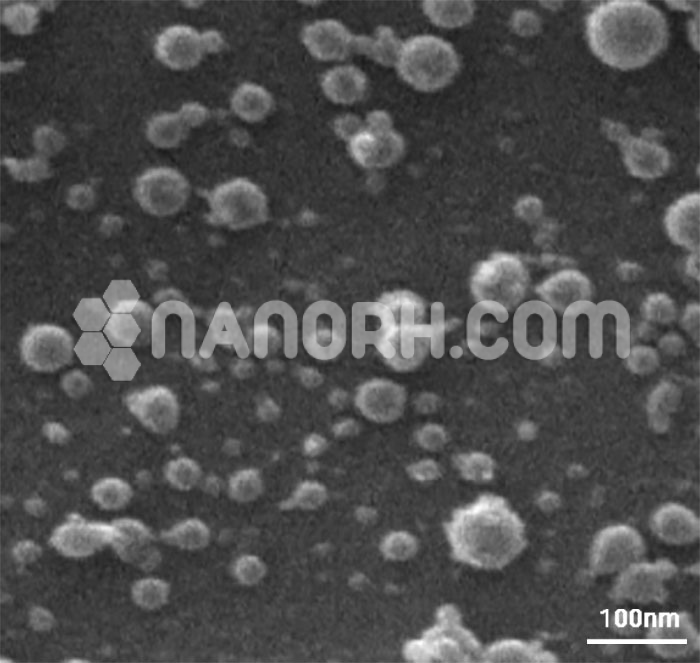
| Iron Hydroxide Fe(OH)3 Nanoparticles 15wt% Water Dispersion | |
| Product No | NRE-23031 |
| CAS No. | 18624-44-7 |
| Formula | Fe(OH)3 |
| Molecular Weight | 106.867 g/mol |
| APS | <5nm (can be customized) |
| Purity | 99.9% |
| Color | Dark Orange |
| Density | 4.25 g/cm³ |
| Solvent | as per requirement |
| pH | NA |
Iron Hydroxide Nanoparticles / Fe(OH)3 Nanopowder 15wt% Water Dispersion
Introduction
Iron hydroxide nanoparticles / Fe(OH)3 nanopowder 15wt% water dispersion particularly in forms such as goethite (α-FeO(OH)) and ferrihydrite (5Fe₂O₃·9H₂O), are nanoscale materials characterized by their high surface area, reactivity, and versatility. These nanoparticles can be synthesized through methods like co-precipitation, sol-gel processes, and hydrothermal techniques. Their unique properties enable a wide range of applications in environmental science, biomedicine, and materials engineering.
Applications
Environmental Remediation:
Heavy Metal Removal: Effective in adsorbing heavy metals (e.g., lead, cadmium) from contaminated water, making them valuable in water treatment processes.
Phosphate Removal: Used in wastewater treatment to reduce phosphate levels, helping to mitigate eutrophication in aquatic ecosystems.
Biomedical Applications:
Drug Delivery: Functionalized iron hydroxide nanoparticles can serve as carriers for targeted drug delivery, improving the efficacy of treatments.
MRI Contrast Agents: Their magnetic properties allow them to be used as contrast agents in magnetic resonance imaging, enhancing image quality.
Catalysis:
Catalytic Reactions: Act as catalysts in various chemical reactions, including organic synthesis and environmental remediation processes, improving reaction rates and selectivity.
Energy Storage:
Batteries: Investigated as anode materials in lithium-ion batteries, offering potential improvements in energy capacity and stability.
Supercapacitors: Their high surface area contributes to efficient charge storage capabilities.
Sensors:
Environmental Sensors: Used in the development of sensors for detecting pollutants and hazardous materials in the environment.
Biosensors: Can be integrated into biosensors for the detection of biological markers, enhancing sensitivity and specificity.
Pigments and Coatings:
Colorants: Utilized in various industries as pigments due to their color properties and stability.
Protective Coatings: Improve corrosion resistance and durability in coatings for industrial applications.
Agriculture:
Soil Amendments: Enhance soil health and nutrient availability, promoting better plant growth.
Controlled Release Fertilizers: Can be used to improve the efficiency of fertilizer delivery to plants.
Textiles:
Antimicrobial Properties: Incorporated into fabrics to provide antibacterial and antifungal effects, improving hygiene and longevity.