| Iron Carbide Nanoparticles | |
| Product No | NRE-5116 |
| CAS No. | 12127-45-6 |
| Formula | Fe5C2 |
| APS | <100nm (Can be Customized) |
| Purity | 99.9% |
| Color | Black/ Dark Green |
| Density | NA |
| Molecular Weight | 303.2464 g/mol |
| Melting Point | NA |
| Boiling Point | NA |
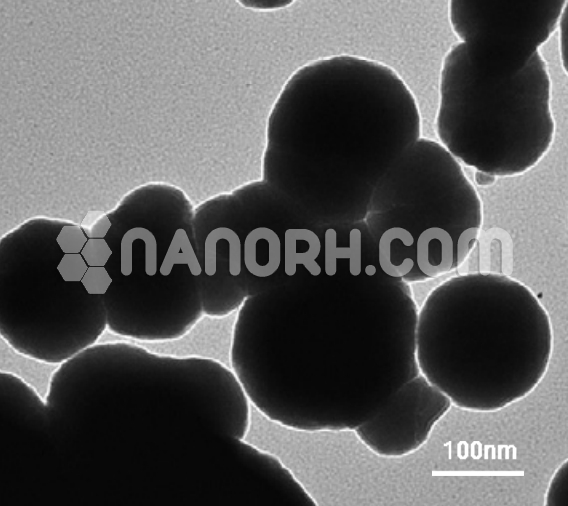
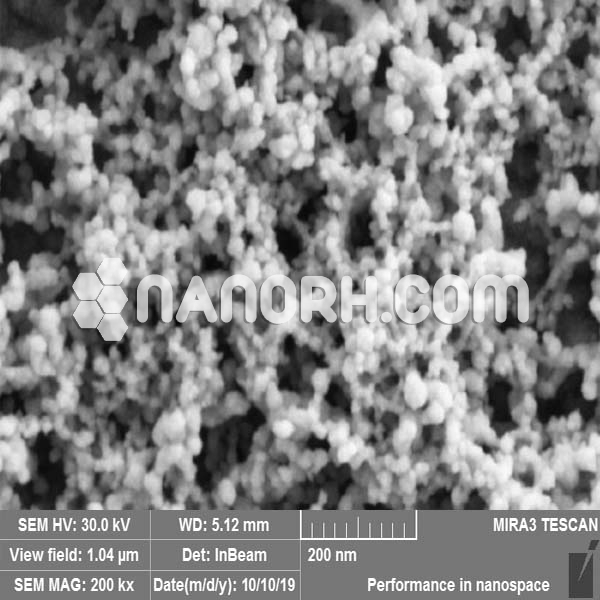
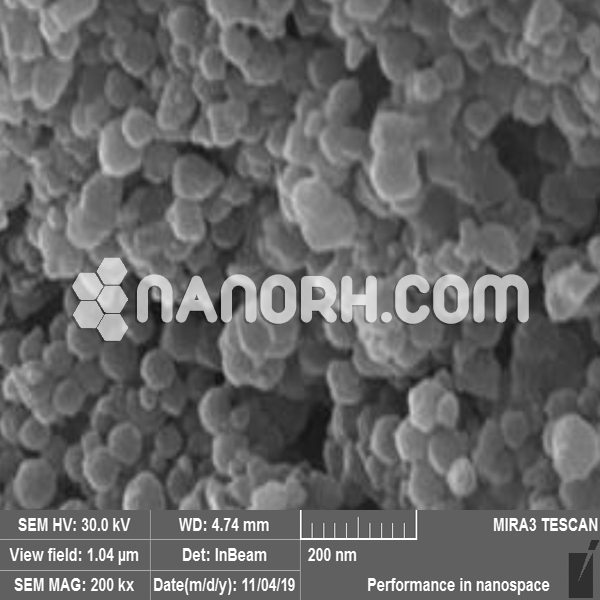
Iron Carbide Nanoparticles
Introduction
Iron carbide nanoparticles often referred to as cementite, is an iron-carbon compound that plays a significant role in metallurgy, particularly in the context of steel and cast iron. When iron carbide is reduced to nanoparticle form, it exhibits enhanced properties, including increased surface area, reactivity, and catalytic activity. These nanoparticles are typically synthesized using methods such as chemical vapor deposition (CVD), sol-gel processes, and hydrothermal synthesis, allowing precise control over their size, shape, and dispersion.
Iron carbide nanoparticles are of particular interest due to their unique electronic, magnetic, and catalytic properties. These characteristics make them suitable for a wide range of applications in energy, catalysis, environmental remediation, and nanotechnology.
Properties
Magnetic Properties:
Iron carbide nanoparticles exhibit strong magnetic properties due to the presence of iron, a magnetic metal. These properties are particularly valuable in applications like magnetic storage, sensors, and bio-magnetic separation.
The magnetic behavior of can be tuned by controlling their size and shape at the nanoscale.
Catalytic Properties:
Are excellent catalysts in several chemical reactions, particularly in hydrogenation, Fischer-Tropsch synthesis (for converting CO and H₂ into hydrocarbons), and CO₂ reduction. The presence of carbon in the compound enhances the ability of iron carbide to facilitate these reactions.
Applications
Catalysis:
Fischer-Tropsch Synthesis: Iron carbide nanoparticles are widely used as catalysts in Fischer-Tropsch synthesis, a method for converting syngas (a mixture of CO and H₂) into hydrocarbons, such as liquid fuels. The catalytic properties of iron carbide are advantageous in producing high yields of hydrocarbons while minimizing byproducts.
Hydrogenation Reactions: Iron carbide nanoparticles are used as catalysts in hydrogenation reactions, where unsaturated organic compounds (like alkenes) are converted into saturated hydrocarbons. This is particularly important in the petrochemical industry for refining processes.
CO₂ Reduction: These nanoparticles are also employed in electrochemical CO₂ reduction, where they help convert CO₂ into useful chemicals, such as carbon monoxide or hydrocarbons, offering potential for sustainable carbon capture and utilization technologies.