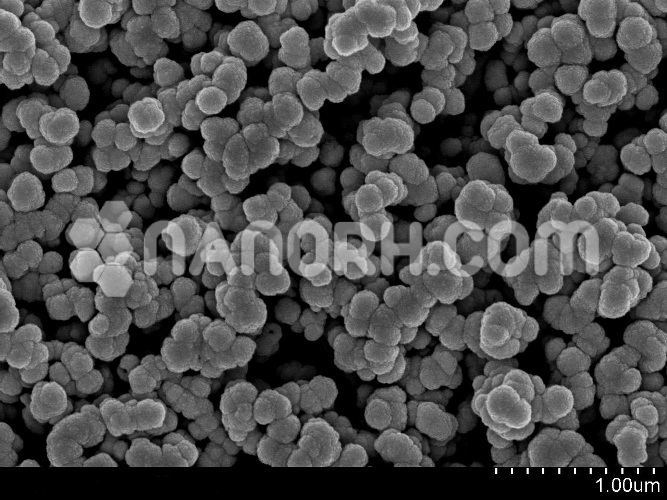
| Indium Selenide Nanoparticles | |
| Product No | NRE-25007 |
| CAS | 12056-07-4 |
| Purity | >99% |
| Molecular Formula | In2Se3 |
| Molecular Weight | 466.516 g/mol |
| Color | Gray Black |
| Density | 5.80 g/cm³ |
| APS | <100nm (can be customized) |
| Melting Point | 600 °C |
| Boiling Point | NA |
Indium Selenide Nanoparticles
Indium selenide ( In2Se3) nanoparticles are notable for their unique electronic, optical, and material properties, making them suitable for various advanced applications.
Optoelectronic Devices: In2Se3 nanoparticles are used in optoelectronic devices due to their semiconductor properties. They are employed in applications such as photodetectors, light-emitting diodes (LEDs), and laser devices. Their ability to absorb and emit light in the visible to near-infrared spectrum is particularly useful in these applications.
Photovoltaics: In2Se3 nanoparticles can be used in thin-film solar cells. Their semiconductor properties make them suitable for absorbing sunlight and converting it into electrical energy. Research is ongoing to enhance the efficiency of solar cells incorporating InSe.
Thermoelectric Materials: Due to their unique electronic properties, In2Se3 nanoparticles are explored for use in thermoelectric materials. These materials convert temperature differences into electrical energy or vice versa, useful in energy harvesting and cooling applications.
Catalysis: In2Se3 nanoparticles have potential as catalysts in various chemical reactions. Their high surface area and unique electronic properties can enhance catalytic activity and selectivity, making them suitable for reactions such as hydrogen evolution or organic transformations.
Sensing Applications: In2Se3 nanoparticles can be used in sensors for detecting gases, pollutants, and biological molecules. Their sensitivity and the ability to modify their electronic properties make them effective in a range of sensing applications.
Biomedical Applications: In2Se3 nanoparticles are studied for their potential in biomedical imaging and therapy. Their optical properties can be harnessed for imaging techniques like fluorescence microscopy, and their biocompatibility is explored for drug delivery systems.
Nanocomposites: In2Se3 nanoparticles can be incorporated into various nanocomposites to enhance mechanical, electrical, or thermal properties. These composites find applications in advanced materials and coatings.
Electronic Devices: The high electron mobility and low bandgap of In2Se3 make it suitable for use in high-performance electronic devices such as transistors and memory devices. Their integration into flexible and transparent electronics is also being explored.
Nonlinear Optics: Due to their nonlinear optical properties, In2Se3 nanoparticles are investigated for use in devices such as optical switches, modulators, and frequency converters.
Energy Storage: In2Se3nanoparticles are studied for their potential use in energy storage devices like batteries and supercapacitors, where their unique properties could improve energy density and performance.
When working with In2Se3 nanoparticles, it’s important to follow safety protocols, especially considering that selenium compounds can be toxic.