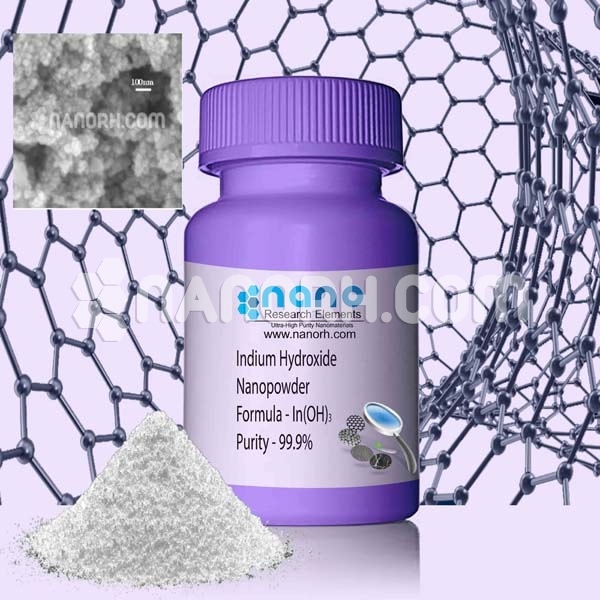
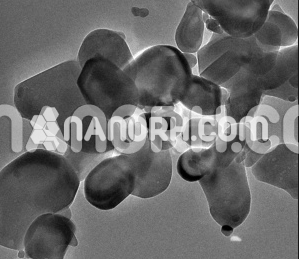
| Indium Hydroxide Nanopowder | |
| Product No | NRE-3025 |
| CAS No. | 20661-21-6 |
| Formula | In(OH)3 |
| APS | <100nm (Can be Customized) |
| Purity | 99.9% |
| Color | white |
| Molecular Weight | 165.84002 g/mol |
| Density | 4.38 g/cm3 |
| Melting Point | 150 °C |
| Boiling Point | NA |
Indium Hydroxide Nanopowder
Applications
Electronics and Optoelectronics
Transparent Conductive Films: Indium Hydroxide nanopowder can be used to produce indium tin oxide (ITO), a highly conductive and transparent material that is widely used in touch screens, solar cells, and LEDs. The nanopowder form enhances the material’s conductivity, transparency, and overall performance.
Semiconductors and Thin-Film Transistors: The nanopowder form of indium hydroxide can be converted into indium oxide (In₂O₃), which is widely used in thin-film transistors, photodetectors, and solar cells due to its excellent semiconducting properties.
Photocatalysis: Indium hydroxide nanopowder can be used in photocatalysis for energy conversion, such as in solar cells. The material’s ability to absorb light and facilitate photoreactions makes it valuable for enhancing energy conversion efficiency.
Catalysis
Catalysts for Organic Synthesis: Indium Hydroxide nanopowder can be utilized as a catalyst or catalyst support in hydrogenation, oxidation, and polymerization reactions. It is especially useful in fine chemical synthesis, where high reactivity and selectivity are required.
Environmental Catalysis: The nanopowder is also useful in environmental catalysis applications, including the degradation of organic pollutants, particularly in water treatment and air purification. It can help to break down contaminants or toxic gases, improving environmental conditions.
Energy Storage and Conversion
Batteries and Supercapacitors: In(OH)3 is studied for use in energy storage devices such as batteries and supercapacitors. The high surface area of the nanoparticles increases the charge storage capacity, making these devices more efficient.
Hydrogen Storage: The ability of indium compounds to absorb hydrogen makes indium hydroxide nanoparticles useful in hydrogen storage systems, which is critical for the development of fuel cells and other clean energy applications.
Solar Energy: The conversion of In(OH)3 into indium oxide also opens the door for its use in solar energy devices, particularly in solar cells and photovoltaics, where high conductivity and photonic properties are important.