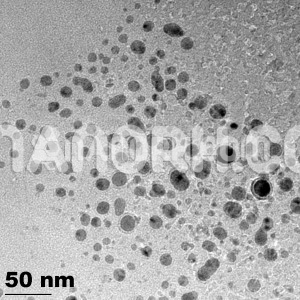
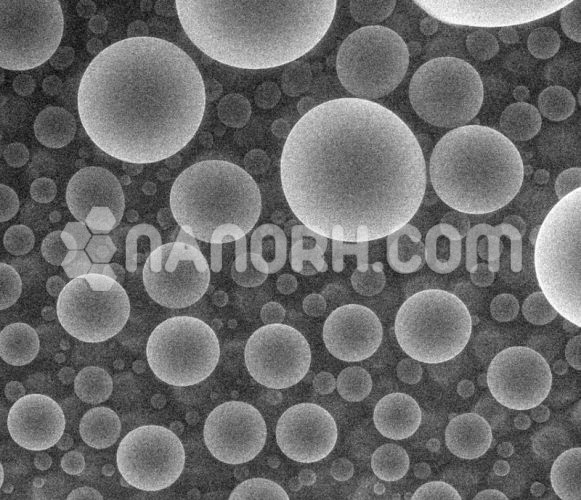
Indium Gallium Arsenide Nanopowder (InGaAs, Purity: 99.9%, APS: <100 nm)
Indium Gallium Arsenide Nanopowder
| Indium Gallium Arsenide Nanopowder | |
| Product No | NRE-25006 |
| CAS | 106097-59-0 |
| Purity | >99.99% |
| Molecular Formula | InGaAs |
| Molecular Weight | 259.46 g/mol |
| Color | White Crystalline Powder |
| Density | 5.68 g/cm³ |
| APS | <100nm (can be customized) |
| Melting Point | 844 °C |
| Boiling Point | NA |
Indium Gallium Arsenide Nanopowder
Indium gallium arsenide (InGaAs) nanopowder combines the properties of indium arsenide (InAs) and gallium arsenide (GaAs), offering a range of unique characteristics that can be harnessed in various advanced applications.
High-Speed and High-Frequency Electronics: InGaAs is renowned for its high electron mobility and saturation velocity, making it ideal for high-speed and high-frequency electronic devices. Applications include high-frequency transistors, microwave detectors, and radio frequency (RF) components.
Infrared Photodetectors: InGaAs is highly effective in the near-infrared (NIR) region of the electromagnetic spectrum. InGaAs nanopowder is used in photodetectors and sensors for NIR imaging, telecommunications, and spectroscopy.
Optoelectronic Devices: InGaAs is used in a variety of optoelectronic devices, including laser diodes, photodiodes, and modulators. These devices are essential for optical communication systems, such as fiber-optic networks, where InGaAs’s ability to operate in the NIR range is beneficial.
Quantum Dot Lasers: InGaAs quantum dots can be used to create lasers that operate in the NIR region. These lasers are important for applications in telecommunications and biomedical imaging.
Solar Cells: InGaAs is used in multi-junction solar cells, which are designed to capture a broader spectrum of sunlight and improve efficiency. InGaAs can be combined with other materials to create high-efficiency photovoltaic devices.
Terahertz Devices: InGaAs can be employed in terahertz technology for generating and detecting terahertz radiation. Applications include imaging, spectroscopy, and security screening.
Thermoelectric Materials: InGaAs nanopowder can be used in thermoelectric deviceswhich convert temperature differences into electrical energy or vice versa. These devices are useful in energy harvesting and cooling technologies.
Biomedical Imaging: Due to its NIR sensitivity, InGaAs is used in biomedical imaging techniques such as optical coherence tomography (OCT) and fluorescence imaging. These applications benefit from the material’s ability to penetrate tissues with minimal absorption.
Environmental Monitoring: InGaAs photodetectors are used in environmental monitoring for detecting gases and pollutants in the NIR range. This includes applications in air quality monitoring and remote sensing.
Catalysis: InGaAs nanopowder may also find applications as a catalyst or in catalytic systems, though this is less common compared to its use in electronic and optoelectronic applications.