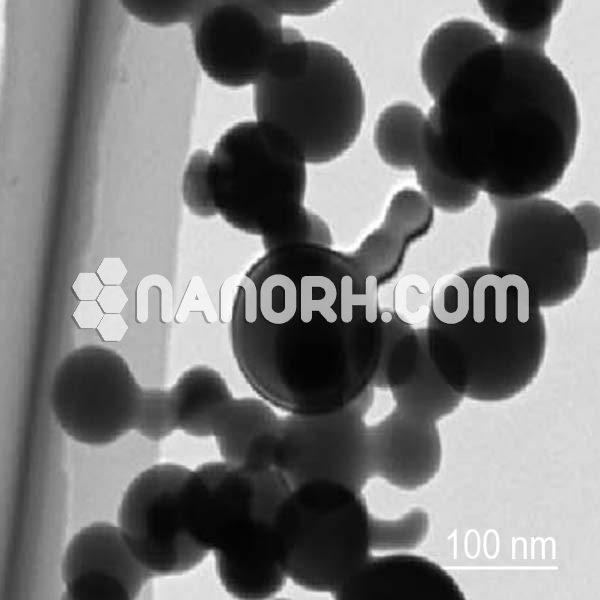
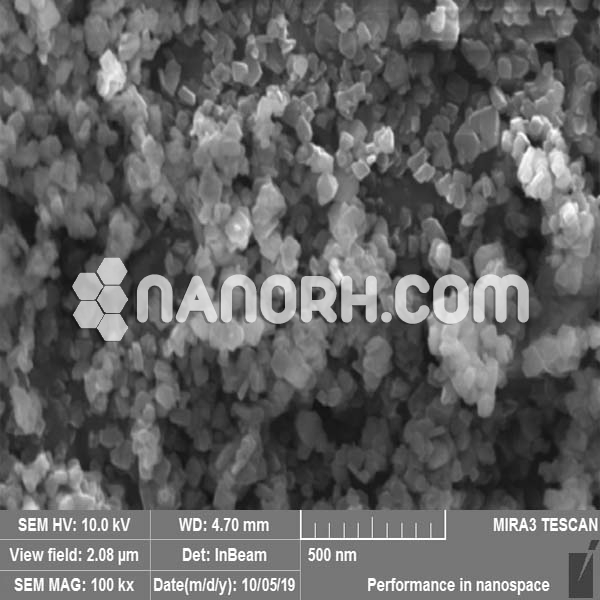
| Indium Bromide Nanoparticles | |
| Product No | NRE-5105 |
| CAS | 13465-09-3 |
| Purity | 99.9% |
| Molecular Formula | InBr3 |
| Molecular Weight | 354.55 g/mol |
| Color | White |
| Density | 4.74 g/cm3 |
| APS | <100 nm (can be customized) |
| Melting Point | 420 °C |
| Boiling Point | NA |
Indium Bromide Nanoparticles
Indium bromide nanoparticles is a compound consisting of indium (In) and bromine (Br), which is typically found as a white crystalline solid in its bulk form. When synthesized as nanoparticles, indium bromide exhibits enhanced electronic, optical, and chemical properties due to the effects of quantum confinement and a high surface-area-to-volume ratio. These nanoparticles have significant potential in various fields, including electronics, optical devices, catalysis, and environmental monitoring.
Applications
Electronics and Semiconductors:
Optoelectronics: Indium bromide nanoparticles are used in optoelectronic devices, including light-emitting diodes (LEDs), photodetectors, and solar cells. Their ability to absorb and emit light efficiently makes them ideal for infrared and visible light applications, where wavelength tuning is needed.
Transistors and Diodes: InBr nanoparticles, due to their semiconductor properties, can be employed in the development of transistors, diodes, and other electronic components. Their high reactivity and small size enable more compact and efficient devices in nanoelectronics.
Catalysis:
Catalytic Reactions: Indium bromide nanoparticles are used as catalysts in chemical reactions, particularly in the synthesis of organic compounds. Their large surface area and chemical reactivity make them highly efficient in heterogeneous catalysis. They can facilitate reactions such as hydrogenation, dehydrogenation, and carbon-carbon coupling reactions.
Environmental Catalysis: are also used in environmental applications for the degradation of pollutants. They can act as catalysts in the breakdown of organic contaminants in industrial waste streams or for water purification.
Sensing and Detection:
Gas Sensing: Due to their high surface reactivity, can be used in the detection of gases, such as carbon monoxide (CO) and ammonia (NH₃).