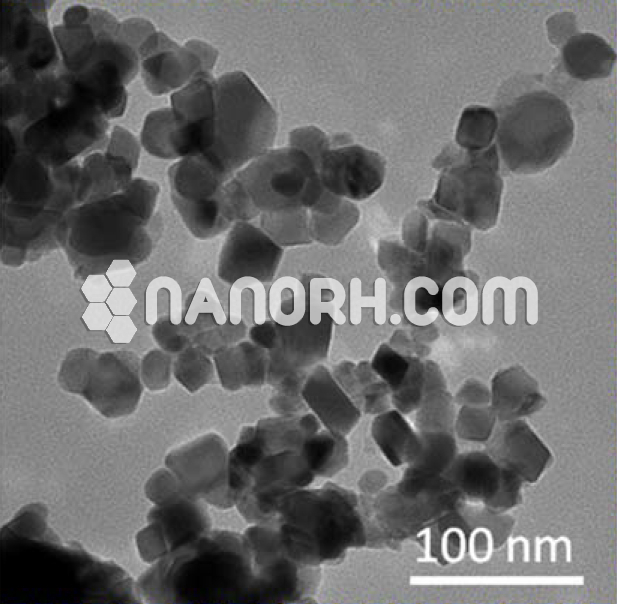
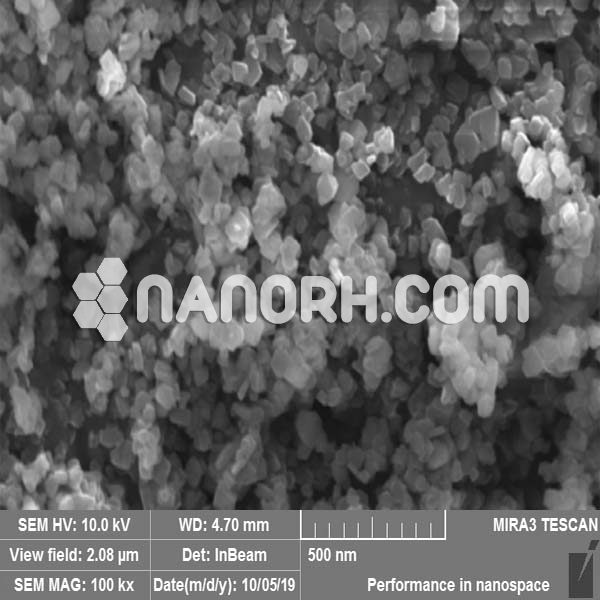
| Indium Antimonide Nanoparticles | |
| Product No | NRE-5104 |
| CAS No. | 1312-41-0 |
| Formula | InSb |
| APS | <100 nm (Can be Customized) |
| Purity | 99.9% |
| Color | Dark grey |
| Molecular Weight | 236.58 g/mol−1 |
| Density | 5.775 g⋅cm−3 |
| Melting Point | 527 °C |
| Boiling Point | NA |
Indium Antimonide Nanoparticles
Applications
Infrared Detectors and Sensors:
Night Vision and Thermal Imaging: Due to their ability to absorb and emit infrared radiation, InSb nanoparticles are widely used in infrared detectors for night vision and thermal imaging devices. They can detect low-intensity infrared radiation emitted by objects, making them useful in military, security, and aerospace applications.
Gas Sensing: InSb nanoparticles are also used in gas sensors, particularly for detecting gases like carbon dioxide (CO₂) and methane (CH₄). Their sensitivity to infrared light allows them to detect the absorption spectra of specific gases.
High-Speed Electronics:
High-Frequency Devices: The high electron mobility of indium antimonide makes it ideal for high-frequency and high-speed electronics, such as high-speed transistors, radio-frequency devices, and microwave components. These applications benefit from InSb’s ability to perform efficiently at very fast switching speeds.
Transistors and Amplifiers: InSb nanoparticles are explored for transistor and amplifier designs in microelectronics, where they can enhance the performance of integrated circuits (ICs) in high-speed and low-power electronic applications.
Quantum Computing and Spintronics:
Quantum Devices: Indium antimonide nanoparticles have shown promise in quantum computing due to their ability to support quantum dots and quantum states. Their narrow bandgap and quantum effects make them suitable for quantum bit (qubit) development and other quantum technologies.
Spintronics: InSb is of interest in spintronic devices, where the spin of electrons (in addition to their charge) is utilized to store and manipulate data. InSb nanoparticles can be used in spintronic applications for data storage and logic gates, offering advantages in terms of efficiency and miniaturization.
Optoelectronics:
Optical Communication: InSb nanoparticles are used in optoelectronic devices for infrared communication systems. Their ability to operate in the infrared spectrum makes them suitable for fiber-optic communication and telecommunication technologies.
Photodetectors and Photovoltaics: InSb nanoparticles can be integrated into photodetectors and solar cells, particularly in devices designed to detect infrared light or to harvest solar energy. Their sensitivity to infrared radiation allows for the development of infrared photodetectors for applications in solar energy and communication systems.