| Hagg Iron Carbide Nanoparticles | |
| Product No | NRE-5116 |
| CAS No. | 7439-89-6/7440-44-0 |
| Formula | Fe5C2 |
| APS | <100nm (Can be Customized) |
| Purity | 99.9% |
| Color | NA |
| Magnetization | 140 emu/g |
| Coercivity | 703 Oe |
| Shape | Spherical |
| Appearance | Powder |
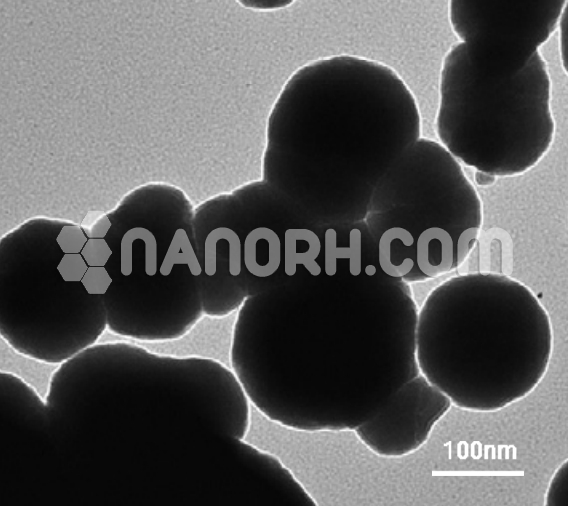
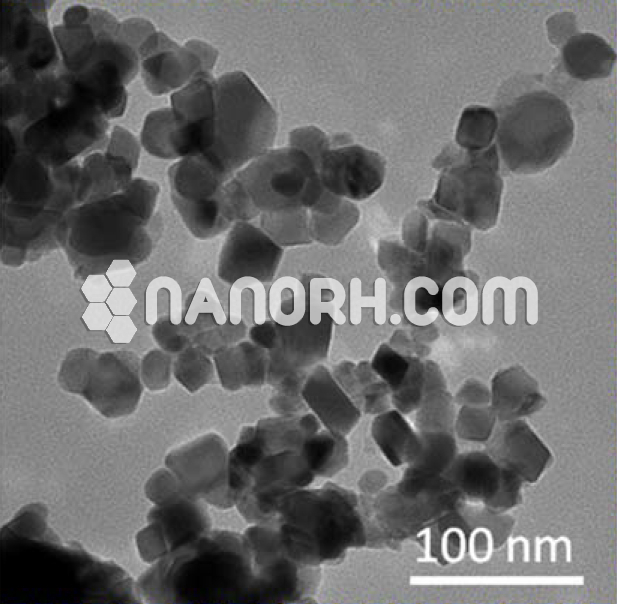
Hagg Iron Carbide Nanoparticles
Hagg iron carbide, commonly referred to as cementite or iron carbide (Fe₃C), is a compound of iron and carbon that plays a key role in the structure and properties of steel and cast iron. Cementite forms when iron combines with carbon in specific proportions and is characterized by its high hardness and brittleness.
Applications
Materials Science and Engineering:
Wear-Resistant Coatings: Fe₃C nanoparticles are used to enhance the wear resistance of materials. When incorporated into coatings or composites, they improve the durability of parts exposed to friction or abrasion, such as in automotive and machinery components, including brake pads, engine parts, and cutting tools.
Hard Metal Alloys: Iron carbide is an essential component of hard steel alloys, such as tool steels and high-carbon steels. The addition of Fe₃C nanoparticles to these alloys enhances their strength, hardness, and resistance to wear and fatigue.
Sintered Materials: In the production of sintered materials, Fe₃C nanoparticles can be used to create hard, durable materials for use in aerospace, automotive, and other heavy industries. These nanoparticles help to improve the performance of sintered alloys by increasing their hardness and reducing friction.
Catalysis:
Hydrocarbon Processing: Fe₃C nanoparticles are used as catalysts or catalyst supports in processes such as Fischer-Tropsch synthesis, where carbon monoxide and hydrogen are converted into liquid hydrocarbons. The high surface area of the nanoparticles enhances the reaction rate and efficiency.
Hydrogenation and Dehydrogenation: Iron carbide nanoparticles can be used in hydrogenation reactions (adding hydrogen to organic compounds) and dehydrogenation (removing hydrogen). These reactions are important in the production of fine chemicals, pharmaceuticals, and biofuels.
Carbon Nanotube Synthesis: Iron carbide nanoparticles can serve as catalysts in the growth of carbon nanotubes (CNTs), which are widely used in electronics, nanotechnology, and materials science.