| Hafnium Chloride Nanoparticles | |
| Product No | NRE-5098 |
| CAS No. | 13499-05-3 |
| Formula | HfCl4 |
| APS | <100nm (Can be Customized) |
| Purity | 99.9% |
| Color | White |
| Molecular Weight | 320.302 g/mol |
| Density | 3.89 g/cm³ |
| Melting Point | 432 °C |
| Boiling Point | NA |
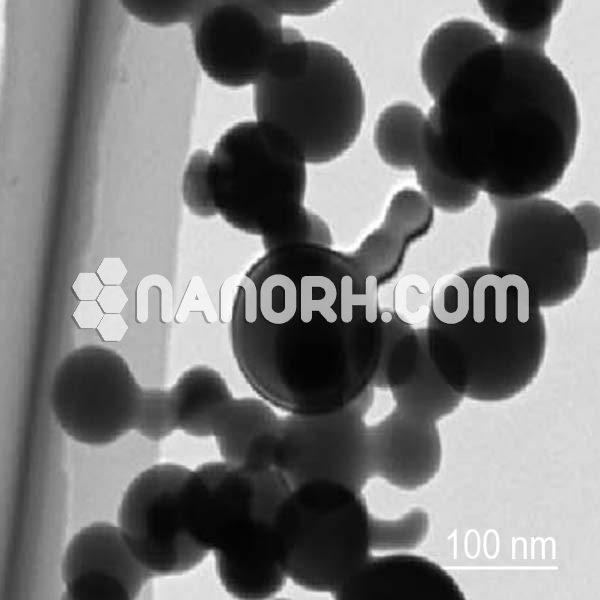
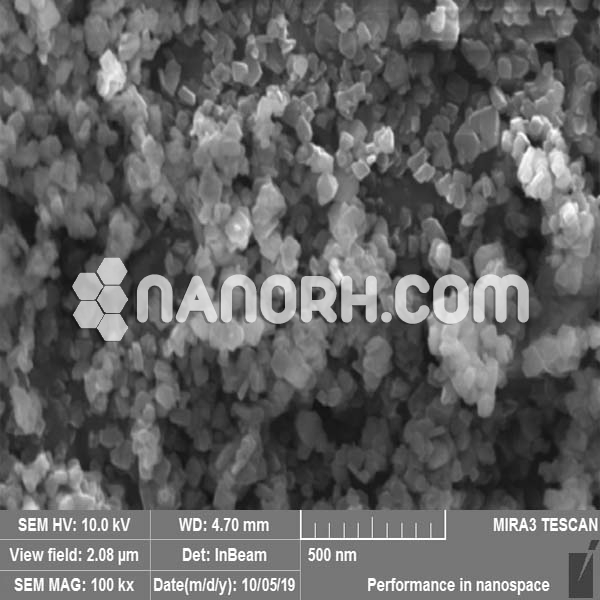
Hafnium Chloride Nanoparticles
Hafnium chloride nanoparticles is a chemical compound composed of hafnium (Hf) and chlorine (Cl). In its solid form, HfCl₄ is typically a white crystalline powder that is highly soluble in organic solvents like benzene and can readily decompose at high temperatures. When reduced to nanoparticle form, hafnium chloride exhibits enhanced properties due to its increased surface area and reactivity compared to bulk materials.
Applications
Semiconductor and Electronics:
Fabrication of Hafnium Oxide Thin Films: HfCl₄ nanoparticles are frequently used in the fabrication of hafnium oxide (HfO₂) thin films. HfO₂ is a high-k dielectric material used in semiconductor devices and transistors, particularly in the production of advanced MOSFETs (metal-oxide-semiconductor field-effect transistors). HfO₂ thin films are essential for improving the performance and scalability of modern microelectronics, especially as the semiconductor industry moves towards smaller node sizes.
Catalysis:
Catalytic Reactions: HfCl4 are used in catalysis, particularly in organic synthesis and chemical reactions that require efficient activation of certain bonds. The high surface area and reactivity of HfCl₄ nanoparticles make them suitable for use in processes such as hydrocracking, hydrogenation, and oxidation reactions.
Hydrogenation Catalysts: HfCl4 along with other hafnium-based materials, can be employed in hydrogenation reactions for producing various chemicals, including fuels and fine chemicals.
Material Science:
Hafnium-Based Ceramics: HfCl4 can be used as precursors to create high-performance hafnium-based ceramics. These materials have applications in areas that require thermal resistance, such as in aerospace and defense technologies. Hafnium ceramics are known for their use in extreme environments due to their excellent thermal stability and mechanical properties.
Refractory Coatings: HfCl4 are utilized in the creation of refractory coatings for applications that require high-temperature resistance. These coatings can be applied to metal surfaces, engines, and aerospace components to protect them from thermal degradation.