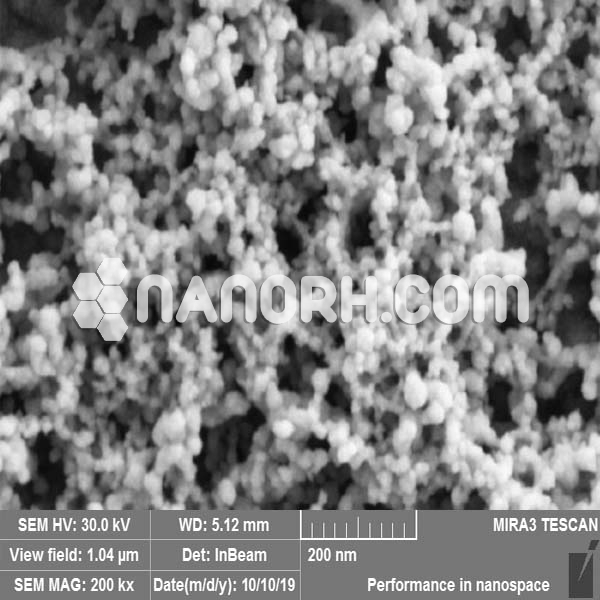
| Hafnium Boride Nanopowder | |
| Product No | NRE-5096 |
| CAS | 12007-23-7 |
| Purity | 99% |
| APS | <100 nm (can be customized) |
| Formula | HfB2 |
| Molecular Weight | 200.112 g/mol |
| Density | 10.5 g/cm3 |
| Color | NA |
| Melting Point | 3250 °C |
| Boiling Point | NA |
Hafnium Boride Nanopowder
Applications
Aerospace and Defense:
Thermal Protection Systems: Due to its extremely high melting point and thermal stability, HfB₂ nanopowder is used in aerospace applications such as thermal protection systems for spacecraft and high-speed vehicles (e.g., re-entry vehicles, hypersonic aircraft). It is used in the production of heat shields and ablative coatings that protect materials from extreme temperatures during high-speed flight or re-entry.
Missile Nose Cones: HfB₂ nanopowder is also used in the development of missile nose cones and other components exposed to high temperatures and frictional heat, providing protection against the intense heat generated during high-speed flight.
Cutting Tools and Abrasives:
Wear-Resistant Coatings: Due to its exceptional hardness, HfB₂ nanopowder is used in abrasive applications, such as in the manufacturing of cutting tools and wear-resistant coatings. These coatings can be applied to components in harsh mechanical environments, improving their longevity and performance.
Grinding and Cutting: HfB₂-based composites are also used in grinding wheels, drill bits, and other tools that experience high wear, helping to extend tool life.
High-Temperature Electronics:
Electrical Conductors: The electrical conductivity of HfB₂ makes it useful in high-temperature electronics, including components such as resistors, capacitors, and heating elements that must operate in extreme conditions. It can be used in electronic circuits and sensors designed for use in harsh environments.
Semiconductor Devices: HfB₂ nanopowder is also being explored for use in semiconductor applications where high temperatures are present, such as in power electronics or optoelectronics that require materials capable of withstanding high thermal loads.