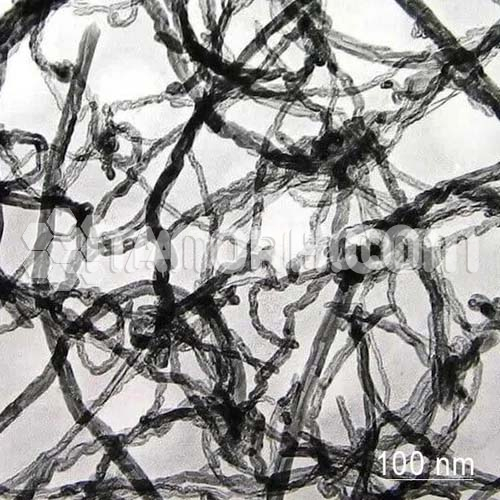
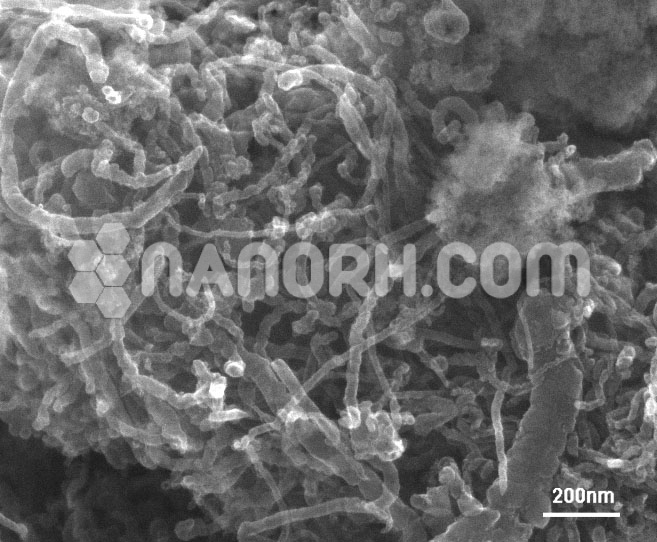
Graphene Iron Nanoparticles / Graphene Iron Nanopowder
The product is composed of highly electric conductive graphene and nickel magnetic nanopowder. The nickel magnetic nanopowder / nanoparticles can not only prevent dispersed graphene from reagglomerating, but also exhibit synergetic effect with graphene. By mixing the two conductive products, it can effectively improve the electrical conductivity, thermal conductivity and mechanical properties; effectively enhance tensile strength, hardness and elastic modulus characteristics, and provide higher electrode conductivity and stronger electrode mechanical strength and adhesive attraction. Also, can obtain magnetic nano-materials in the application of magnetic recording and coatings.
| Graphene Iron Nanoparticles | |
| Product No | NRE-39007 |
| CAS No. | NA |
| Purity | >99wt% |
| Average Diameter | 1 μm – 12 μm |
| Average Length | NA |
| Special Surface Area(SSA) | 500 – 1200m2/g |
| Tap Density | 1.2 gram/cm |
| True Density | NA |
| Electric Conductivity | 1000-1500 S/M |
Graphene Iron Nanoparticles
Potential Applications: screen displays, electric motors, sensing devices, aerospace and automotive devices, body armor and tear-resistant cloth fibers and textile products, sports equipment. Serve as a conductive metallic or semiconductor, conductive films in coatings, plastics, certain bioscience applications, solar and electronic applications, additives in polymers, catalysts, electron field emitters for cathode-ray lighting elements, flat panel display, gas-discharge tubes in telecom networks, electromagnetic-wave absorption, and shielding, energy conversion; lithium-battery anodes, hydrogen storage, nanotube composites (by filling or coating), nanoprobes for STM, AFM, and EFM tips, nanolithography; nanoelectrodes, drug delivery, sensors, reinforcements in composites, supercapacitor. And, other application: (1) additives in polymers; (2) catalysts; (3) electron field emitters for cathode-ray lighting elements; (4) flat panel display; (5) gas-discharge tubes in telecom networks; (6) electromagnetic-wave absorption and shielding; (7) energy conversion; (8) lithium-battery anodes; (9) hydrogen storage; (10) graphene composites (by filling or coating); (11) graphene for STM, AFM, and EFM tips; (12) nanolithography; (13) nanoelectrodes; (14) drug delivery; (15) sensors; (16) reinforcements in composites; (17) supercapacitor.