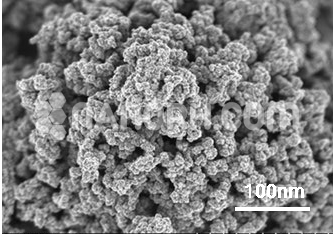
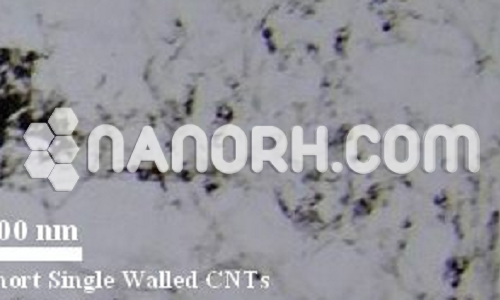
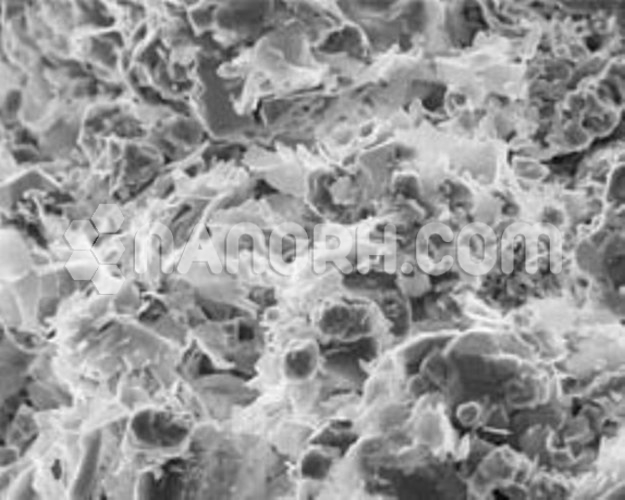
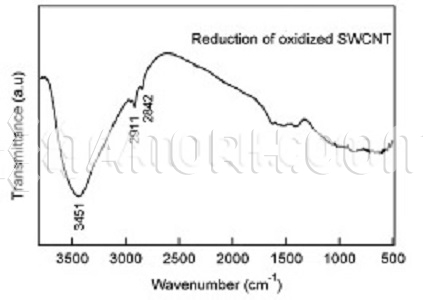
| Graphene Carbon Nanotubes | |
| Product No | NRE-39003 |
| CAS No. | NA |
| Purity | > 97% |
| Average Diameter | >55 nm |
| Average Length | 10-30 um (TEM) |
| Special Surface Area(SSA) | > 60 m2/g (BET) |
| Tap Density | 0.12 g/cm3 |
| True Density | 2.1 g/cm3 |
| Electric Conductivity | >100 s/cm |
Graphene Carbon Nanotubes
Graphene carbon nanotubes are two ground breaking materials in the world of nano technology and materials science. These materials have opened up exciting possibilities in fields ranging from electronics to energy storage, medicine, and even space exploration. Let’s explore what graphene and carbon nanotubes are, how they are created, and their remarkable properties.
Electronics and Optoelectronics
Transistors and Semiconductors: Both graphene and carbon nanotubes are used to create high-performance field-effect transistors (FETs). CNTs, for example, can outperform traditional silicon-based transistors in terms of speed and power efficiency. Graphene’s high electron mobility makes it ideal for ultra-fast transistors.
Flexible Electronics: Graphene is particularly valuable in flexible displays, sensors, and wearable electronics. Because it is highly conductive and flexible, it can be integrated into bendable or stretchable devices without losing performance.
Photodetectors and Solar Cells: Graphene and CNTs are also being used to create more efficient photovoltaic cells (solar cells) and photodetectors, as they absorb light over a wide spectrum and have high charge carrier mobility.
Energy Storage and Conversion
Supercapacitors: Graphene and CNTs are widely used in the design of supercapacitors, which store energy and deliver rapid bursts of power. Due to their high surface area and conductivity, both materials offer enhanced performance over conventional capacitors.
Batteries: In lithium-ion and lithium-sulfur batteries, graphene and CNTs are used to enhance the conductivity and stability of the electrodes, improving the overall battery performance, lifespan, and charging speed.
Fuel Cells: These materials are also used in fuel cells, especially as catalysts or in electrodes, to improve efficiency and durability.
Sensors
Gas Sensors: Graphene and CNTs are highly sensitive to chemical environments, making them useful for gas detection, environmental monitoring, and wearable health sensors. For example, CNT-based sensors can detect gases like NO₂, NH₃, and CO₂ at very low concentrations.
Biosensors: Graphene-based biosensors can be used for detecting specific biomolecules, such as proteins or DNA, with high sensitivity. This makes them useful for medical diagnostics and lab-on-a-chip devices.
Materials and Composites
Strong, Lightweight Composites: Graphene and CNTs are used in creating composites that are both lightweight and exceptionally strong. These composites are used in aerospace, automotive, and construction materials. Graphene, for example, is used in the development of advanced lightweight materials that improve the strength-to-weight ratio of vehicles and structures.
Smart Textiles: Graphene and CNTs are incorporated into fabrics to create “smart” textiles with conductive properties, enabling applications in wearable electronics and health monitoring.
Medical Applications
Drug Delivery Systems: CNTs and graphene oxide (GO) are being investigated for their potential in targeted drug delivery. Their high surface area allows them to carry large quantities of drugs, while their functionalization with biomolecules ensures targeted delivery to specific cells or tissues.
Biomedical Imaging: Graphene and CNTs can be used in imaging techniques such as MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) and CT (computed tomography) due to their ability to interact with electromagnetic fields.
Tissue Engineering: Graphene and CNTs can provide scaffolding for tissue engineering. Their mechanical properties help create structures that mimic natural tissues, which can be used in regenerative medicine.
Water Purification
Desalination: Graphene oxide membranes have shown promise for water desalination due to their ability to filter water at the nanoscale, allowing for faster and more efficient desalination processes.
Water Filtration: CNTs can be used to remove organic contaminants, bacteria, and heavy metals from water, as they are highly porous and have strong adsorption properties.
Thermal Management
Heat Dissipation: Both graphene and CNTs are exceptional thermal conductors. They are used in the design of heat sinks, thermal interfaces, and materials for electronics that require efficient heat management. This can improve the performance and lifespan of electronic devices.
Thermal Coatings: Graphene-based coatings can be applied to surfaces to enhance their heat resistance, which is valuable for applications in high-performance aerospace and automotive industries.
Quantum Computing
Quantum Dots: CNTs and graphene are being explored for their potential in quantum computing, where quantum dots made from these materials could play a role in developing quantum bits (qubits) for more powerful computing systems.
Spintronics: Due to their spin-polarized charge carriers, graphene and CNTs are also being investigated for use in spintronic devices, which exploit the intrinsic spin of electrons to process information in novel ways.