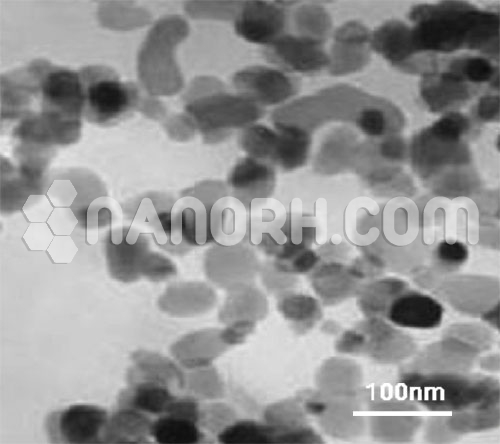
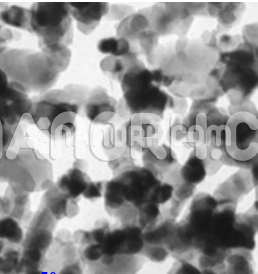
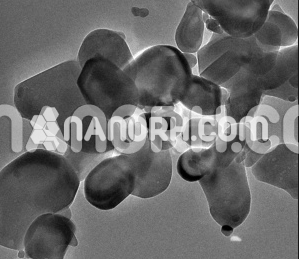
| Gallium Sulfate Nanoparticles | |
| Product No | NRE-5088 |
| CAS No. | 13494-91-2 |
| Formula | Ga2(SO4)3 |
| APS | <100nm (Can be Customized) |
| Purity | 99.9% |
| Color | White |
| Molecular Weight | 427.63g/mol |
| Density | 3.86 g/cm3 |
| Melting Point | 749 °C |
| Boiling Point | NA |
Gallium Sulfate Nanoparticles
Gallium sulfate nanoparticles are nanoparticles made from gallium sulfate, a chemical compound consisting of gallium (Ga) and sulfate (SO₄²⁻) ions. Gallium, a metal found in trace amounts in the Earth’s crust, is widely used in electronic applications due to its semi-conductive properties. When synthesized into nanoparticles, gallium sulfate exhibits distinct physical and chemical properties compared to its bulk counterpart.
Applications
Medical and Biomedical Applications:
Cancer Treatment: Gallium-based compounds, including have shown promise in cancer therapy. Gallium ions can interfere with the growth of cancer cells by inducing apoptosis (programmed cell death). Ga2(SO4)3 Can be used as carriers for targeted drug delivery or as standalone agents for photothermal therapy, where they absorb light and convert it into heat to destroy cancerous cells.
Antimicrobial Activity: Gallium compounds exhibit antimicrobial properties. have been studied for their ability to fight against bacteria and fungi, offering a potential alternative to traditional antibiotics in combating infections, particularly in an era of rising antibiotic resistance.
Imaging and Diagnostics: Ga2(SO4)3 can be used in medical imaging, such as in X-ray imaging or MRI contrast agents, to improve the visibility of tissues or organs for diagnostic purposes. The unique optical and electronic properties of nanoparticles enable enhanced imaging resolution.
Energy Storage and Conversion:
Catalysts in Energy Conversion: are explored as catalysts for reactions such as hydrogen production, which can be part of renewable energy technologies. Their high surface area makes them effective for catalytic processes in fuel cells and other energy conversion systems.
Lithium-Ion Battery Technology: Gallium-based nanoparticles, including gallium sulfate, have been studied for their potential use in energy storage devices such as lithium-ion batteries. They can be used as part of the electrodes to enhance the performance, stability, and capacity of batteries.