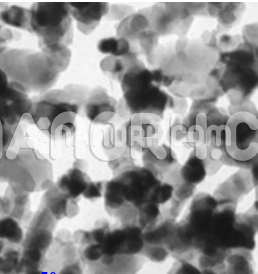
| Gallium Indium Alloy Nanoparticles | |
| Product Number | NRE-2061 |
| CAS No. | 7440-55-3 / 7440-74-6 |
| Formula | GaIn |
| Molecular Weight | 184.54 g/mol |
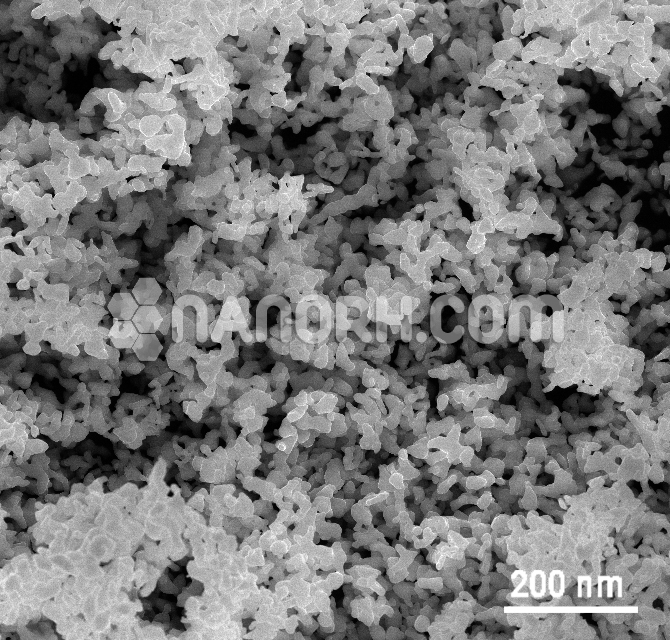
| APS | <100 nm (Can be Customized) |
| Purity | 99.9% |
| Colour | Gray |
| Density | 6.25 g/mL |
| Melting Point | NA |
| Boiling Point | NA |
Gallium Indium Alloy Nanoparticles
Applications
Electronics and Semiconductors
Thermal Interface Materials: Gallium-indium alloy nanoparticles are widely used as thermal interface materials (TIMs) in electronics. These alloys are particularly effective in managing heat dissipation in high-performance computing devices such as CPUs, GPUs, and power semiconductors. Their low melting point allows them to provide superior thermal conductivity between heat sources and heat sinks.
Soldering: The low melting point of gallium-indium alloys makes them highly suitable for soldering applications in electronics. These alloys can form low-temperature solders that are ideal for fine-pitch soldering in advanced electronics, such as in microelectronics and printed circuit boards (PCBs).
Photovoltaic Devices: GaIn can be used in the fabrication of thin-film solar cells and photovoltaic devices. The nanoparticles can improve the efficiency of these devices by enhancing their light absorption and charge transport properties.
Energy Storage and Conversion
Batteries and Supercapacitors: GaIn are being explored as components of high-performance batteries and supercapacitors. Their high conductivity, stability, and ability to undergo multiple charge-discharge cycles make them suitable for use in lithium-ion batteries, sodium-ion batteries, and energy storage systems that require high efficiency and long lifespan.
Biomedicine
Drug Delivery: Gallium-indium alloy nanoparticles are being studied for their use in drug delivery systems. Their biocompatibility, low toxicity, and ability to be functionalized make them suitable for delivering targeted therapeutic agents to specific locations in the body. They can be engineered to carry drugs and release them in response to external stimuli, such as magnetic fields or pH changes.
Medical Imaging: Due to their biocompatibility and unique optical properties, gallium-indium alloy nanoparticles are used as contrast agents in medical imaging techniques, such as magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and computed tomography (CT). The nanoparticles enhance imaging clarity, helping to identify and diagnose diseases like cancer and cardiovascular conditions.