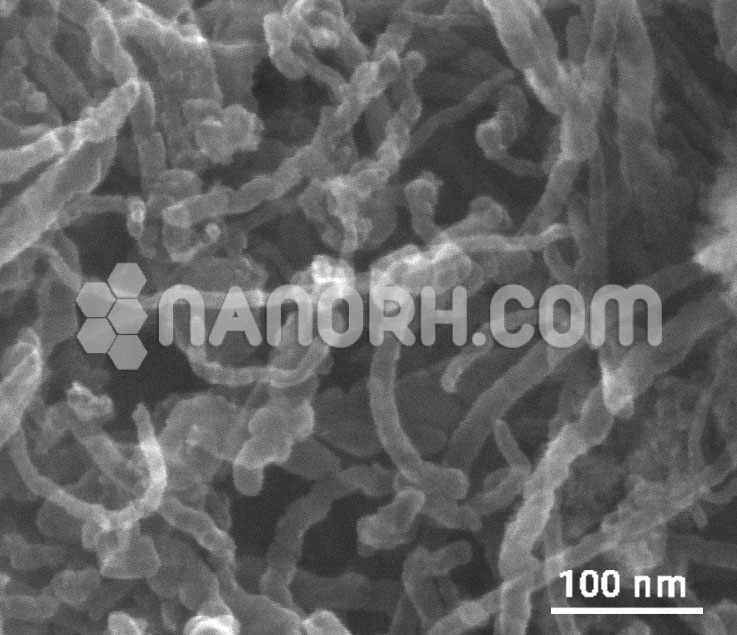
Fullerene Fullerenols 1000ppm Dispersion
Fullerenes are poorly soluble in most solvents and are usually solubilized with aromatic solvents such as toluene, chlorobenzene, or non-aromatic solvents such as carbon disulfide. Pure fullerene solution is usually purple, the concentration is dark purple…
Polyhydroxylated fullerene (Fullerenols) / C60, -OH Functionalized 1000ppm Dispersion
| Product Name | Fullerene C60, -OH Functionalized |
| Product No. | NRE-24063 |
| CAS | 99685-96-8 |
| Purity | >99.9% |
| Melting Point | >280 °C |
| Morphology | Spherical |
| Flash Point | > 94 °C |
| Density | 1.6 g/cm³ at 20 °C |
| Molecular Formula | C60 |
| Molecular Weight | 720.64 g/mol |
| Form | Crystalline powder |
| Orbital energy | HOMO 6.1-6.2 eV |
| Orbital energy | UMO 4.5 eV |
| Reactivity | Non-Reactive/Non-Soluble |
| Stability | Completely Stable |
| Solubility | Soluble in organic solvents |
Polyhydroxylated fullerene
Fullerenes Solubility: Fullerene Fullerenols are poorly soluble in most solvents and are usually solubilized with aromatic solvents such as toluene, chlorobenzene, or non-aromatic solvents such as carbon disulfide. Fullerene Fullerenols solution is usually purple, the concentration is dark purple.
Applications
Biomedical Applications
Drug Delivery:
Polyhydroxylated fullerenes can be used as drug carriers in targeted drug delivery systems. The hydroxyl groups on the surface of the fullerene can be used to attach various therapeutic molecules, such as anticancer drugs, antiviral agents, or anti-inflammatory drugs. The biocompatibility and water solubility of these functionalized fullerenes enable them to deliver drugs efficiently to specific tissues or cells, especially when combined with targeting ligands for site-specific delivery.
Antioxidants:
Due to their radical-scavenging properties, polyhydroxylated fullerenes, especially those with a high number of hydroxyl groups, have potential as antioxidants in treating diseases associated with oxidative stress, such as neurodegenerative disorders (e.g., Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson’s disease) and cardiovascular diseases. The C₆₀(OH)₄ molecule has shown the ability to neutralize free radicals, which can protect cells from damage caused by oxidative stress.
Imaging and Diagnostic Tools:
Polyhydroxylated fullerenes can be conjugated with fluorescent markers or radioisotopes to serve as imaging agents in medical diagnostics. For instance, fluorescent fullerene derivatives can be used in fluorescence microscopy to track cellular processes or in MRI and CT imaging when tagged with appropriate contrast agents. The high surface area and modifiability of polyhydroxylated fullerenes allow for easy conjugation with various diagnostic molecules.
Gene and RNA Delivery:
Functionalized fullerenes can serve as vectors for gene delivery or RNA interference. Polyhydroxylated fullerenes can be engineered to encapsulate genetic material, such as DNA or RNA, and deliver it to cells for gene therapy or gene silencing applications. The solubility and biocompatibility of polyhydroxylated fullerenes make them promising candidates for non-viral gene delivery systems.