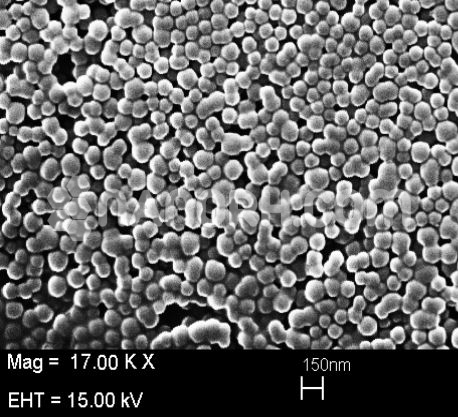
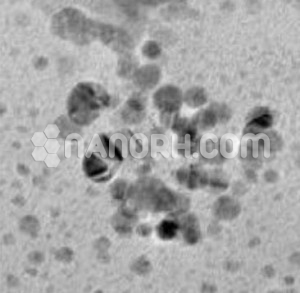
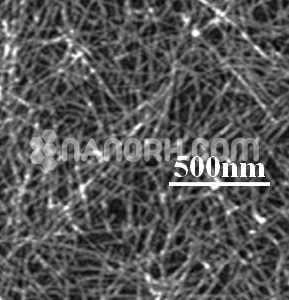
Diamond (C) Nanoparticles Water Dispersion (3-10nm, 5wt% in Water)
High precision polishing-for the computer disk heads, the panels, and chips, optics lenses and jewelery; Additives in Polymer complexes-can be used as a additives in rubber, glass, ceramic, and textile fabric material; Erosion-resistant diamond films/coatings; Biomedical materials (artificial bones and joints);
| Diamond (C) Nanoparticles Water Dispersion | |
| Product No | NRE-22040 |
| CAS No. | 7782-40-3 |
| Formula | C |
| Molecular Weight | 12.01 g/mol |
| APS | <10 nm (can be customized) |
| Purity | > 98.3% |
| Color | Grey |
| Density | 3.51 gm/cm3 |
| Solvent | Water (as per requirement) |
| pH | NA |
Diamond (C) Nanoparticles Water Dispersion
High precision polishing-for the computer disk heads, the panels, and chips, optics lenses and jewelry; Additives in Polymer complexes-can be used as an additive in rubber, glass, ceramic, and textile fabric material; Erosion-resistant diamond films/coatings; Biomedical materials (artificial bones and joints); Biosensors; Chemical Sensors; Field electron emission materials; Heat-resistant diamond films/coatings; Integrated circuit substrates; Photoelectric sensors; Self-lubricating, wear-resistant composite coating; Pressure-limiting sensors; Radiation-resistant diamond films/coatings; Reinforcing agents for rubber, plastics, and resin; Seed crystal for growing larger diamond; High-strength abrasive material……
Applications
Biomedical Applications
Drug Delivery: One of the most promising uses of diamond nanoparticles in water dispersion is in drug delivery systems. Nanodiamonds can be loaded with therapeutic agents (e.g., chemotherapy drugs) and delivered to specific sites in the body. The hydrophilic nature of water-based dispersions enhances their compatibility with biological systems, making them ideal for targeted drug delivery. Additionally, their surface can be functionalized with specific ligands to increase their affinity for targeted cells, such as cancer cells or infected tissues.
Bioimaging: Nanodiamonds can be used as contrast agents in medical imaging techniques such as fluorescence microscopy, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), and computed tomography (CT). Their small size and high surface area make them highly effective for imaging, and when dispersed in water, they can be used in vivo without causing toxicity or aggregation.
Wound Healing: Water-dispersed nanodiamonds have shown promise in wound healing applications. Their anti-inflammatory properties and ability to stimulate collagen production can accelerate tissue regeneration and reduce infection risk. They are often used in topical formulations such as ointments or creams, where they can be applied directly to the skin.
Biosensors: Water-dispersed nanodiamonds are used in the development of biosensors to detect biological markers, pathogens, or environmental toxins. Their high surface area allows for the functionalization of specific receptors or antibodies, making them highly sensitive and specific for detecting disease markers or contaminants in water or blood samples.
Electronics and Nanocomposites
Thermal Management: Nanodiamonds are highly efficient at conducting heat, which makes them ideal for applications in thermal management. In electronics, where overheating is a common issue, diamond nanoparticles dispersed in water-based fluids can be used to improve heat dissipation in devices such as microprocessors, LEDs, and power transistors. This leads to better performance and longer device lifespans.
Conductive Materials: When dispersed in water, diamond nanoparticles can be incorporated into conductive inks or nanocomposites used in printed electronics, wearable devices, or flexible electronics. Their electrical conductivity and mechanical strength enhance the performance of these materials, which are used in flexible displays, solar cells, and touchscreens.
Batteries and Supercapacitors: In energy storage devices such as batteries and supercapacitors, nanodiamonds can be used to improve charge retention and conductivity. Water-dispersed diamond nanoparticles can be incorporated into electrodes to enhance the efficiency and longevity of energy storage devices, particularly in lithium-ion batteries and supercapacitors.
Catalysis and Environmental Protection
Catalysts for Chemical Reactions: Diamond nanoparticles dispersed in water can be used as catalysts or catalyst supports in a wide range of chemical reactions, including hydrogenation, oxidation, and polymerization. Their high surface area and chemical stability make them effective for accelerating reactions, while their water-based dispersion allows them to be easily incorporated into industrial processes.