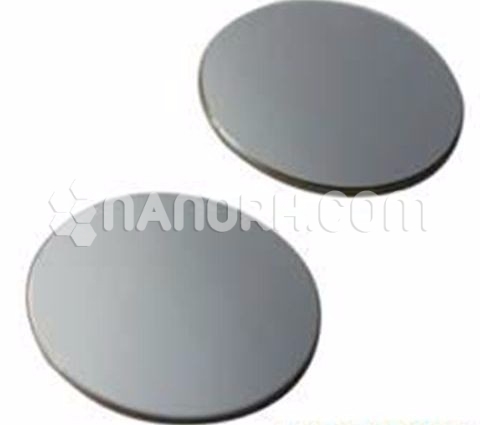
Copper Single Crystal Substrates
Copper Single Crystal Substrates
| Copper Single Crystal Substrates | |
| Product No | NRE-450120-1 |
| CAS | 7440-50-8 |
| Purity | >99.99% (oxygen < 80 ppm) |
| Material | Cu-<100>,/<111>,/<110> |
| Dimensions | 10x10x0.5 |
| Cu Single Substrate Orientation | <100>,/<111>,/<110> |
| Structure | Cubic |
| Thickness | 0.5 mm |
| Polished | Single Side Polished |
| Orientation | +/-2° |
Copper Single Crystal Substrates
Introduction:
Copper single crystal substrates are highly pure and homogenous materials characterized by a uniform crystal structure throughout the substrate. This uniformity offers exceptional electrical and thermal conductivity, making them valuable in various applications within the electronics and materials science fields.
Applications
Electronic Devices:
Cu are used in the fabrication of high-performance electronic devices, including transistors and integrated circuits, where superior electrical conductivity is essential.
Interconnects in Microelectronics:
They serve as interconnect materials in semiconductor devices, providing reliable pathways for electrical signals and enhancing overall device performance.
Thin Film Deposition:
Cu are often used in thin film deposition processes, where their smooth surfaces and consistent crystallographic orientation improve film quality and adhesion.
Photonics and Optoelectronics:
These substrates are employed in optoelectronic applications, such as light-emitting diodes (LEDs) and laser diodes, where high thermal conductivity is required for efficient heat dissipation.
Materials Research:
In materials science, copper single crystal substrates are utilized for fundamental studies of crystallography, electron behavior, and the effects of surface modifications on material properties.
Catalysis:
Due to their high surface area and reactivity, copper single crystal substrates are investigated in catalysis research, particularly for reactions involving gas-solid interactions.
Surface Science Experiments:
They are valuable in surface science studies, allowing researchers to explore phenomena such as adsorption, surface diffusion, and chemical reactions on well-defined surfaces.
MEMS Devices:
Cu can be used in the fabrication of Microelectromechanical Systems (MEMS), where their mechanical properties contribute to device performance.