| Copper Iodate Nanoparticles | |
| Product No | NRE-5069 |
| CAS | 13454-89-2 |
| Purity | 99.9% |
| Molecular Formula | CuI2O6 |
| Molecular Weight | 413.35 g/mol |
| Color | NA |
| Density | 5.09 g/cm3 |
| APS | <100 nm (can be customized) |
| Melting Point | NA |
| Boiling Point | NA |
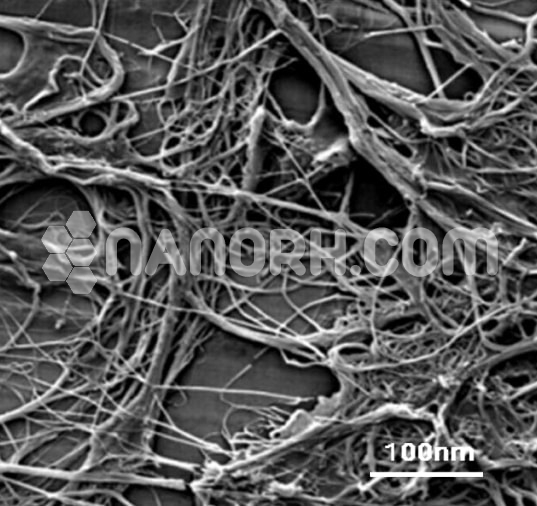
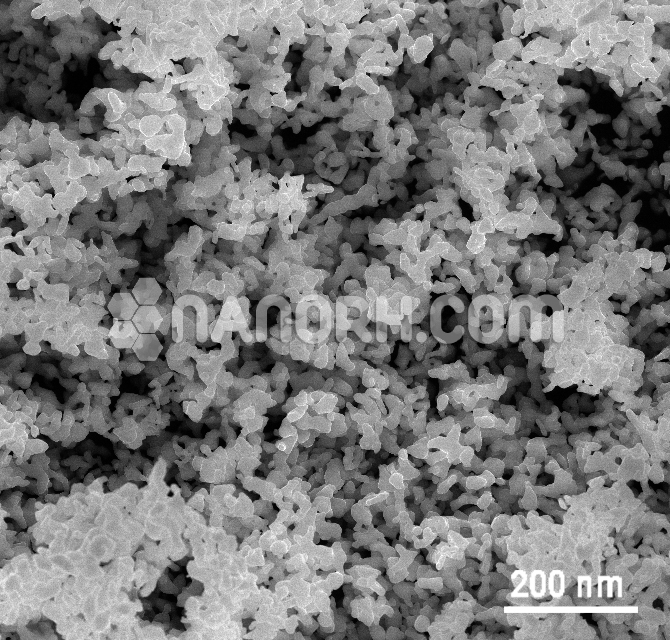
Copper Iodate Nanoparticles
Copper Iodate nanoparticles are a class of metal iodate compounds composed of copper (Cu) and iodate (IO₃) ions. These nanoparticles have attracted significant interest in the field of nanomaterials due to their unique chemical properties, including high reactivity, photocatalytic behavior, and optical characteristics, making them suitable for various industrial and technological applications.
Applications
Photocatalysis and Solar Energy Conversion
Water Splitting: Copper iodate nanoparticles are explored for use in solar water splitting to generate hydrogen, a clean fuel, by using sunlight to break down water molecules into oxygen and hydrogen gas. The photocatalytic properties of copper iodate help in the efficient absorption of light and the catalysis of this reaction, making it a potential material for renewable energy generation.
Pollutant Degradation: The photocatalytic behavior of copper iodate also makes it useful for the degradation of environmental pollutants. Under UV light or sunlight, copper iodate nanoparticles can break down organic contaminants in wastewater treatment processes, including dyes, pesticides, and other hazardous chemicals.
Energy Storage and Conversion
Supercapacitors and Batteries: Due to their electrochemical properties,can be utilized in the development of energy storage devices like supercapacitors and batteries. Their high surface area and stability enhance the charge-discharge efficiency and energy density of these devices, making them useful for high-performance energy storage solutions.
Antibacterial and Biomedical Applications
Antibacterial Activity: Copper is well-known for its antibacterial properties, and copper iodate nanoparticles are no exception. These nanoparticles have been investigated for their potential in disinfection and wound healing applications. They can be used as a part of antibacterial coatings for medical devices, bandages, and implants, helping prevent infection and promoting faster healing.
Drug Delivery: Copper iodate nanoparticles, particularly those with enhanced surface properties, can be functionalized for use in drug delivery systems. Their small size allows them to effectively deliver drugs to specific sites in the body, which is particularly useful for cancer therapy and other targeted treatments.