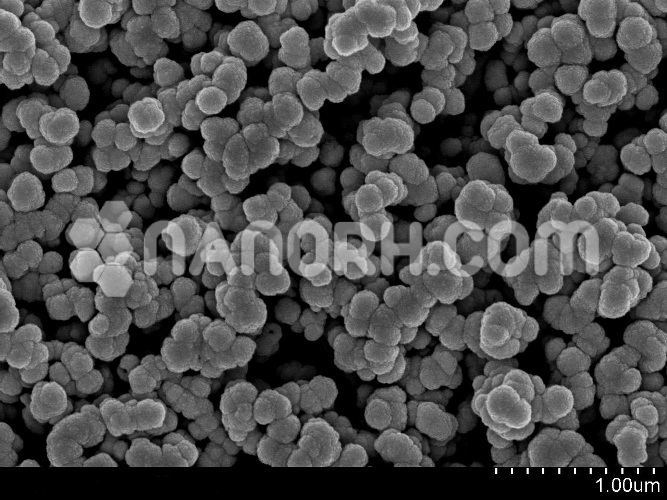
| Copper Indium Gallium Selenide | |
| Product No | NRE-26002 |
| CAS | 12018-95-0 |
| Purity | 98% |
| Molecular Formula | CuInxGa(1-x)Se2 |
| Molecular Weight | 327.05 g/mol |
| Color | Silvery |
| Density | 5.7 g/cm³ |
| APS | <2µm (can be customized) |
| Melting Point | 1,070 to 990 °C |
| Boiling Point | NA |
Copper Indium Gallium Selenide
Copper indium gallium selenide (CIGS) is a compound semiconductor known for its high efficiency and versatility in several applications.
Photovoltaic Cells (Solar Panels)
Thin-Film Solar Cells: CIGS is predominantly used in thin-film photovoltaic cells. Its high absorption coefficient and direct bandgap make it ideal for converting sunlight into electricity with high efficiency. CIGS solar cells are known for their high power conversion efficiency and stability compared to other thin-film technologies.
Optoelectronic Devices
Photodetectors: Due to its efficient light absorption and photoconductive properties, CIGS is used in photodetectors for optical sensing and imaging applications.
Light-Emitting Diodes (LEDs): CIGS can be used in LEDs, particularly those requiring specific wavelengths of light, due to its tunable bandgap.
Semiconductor Technology
Transistors: CIGS is used in thin-film transistors (TFTs) for display technologies, including flat-panel displays. Its semiconductor properties allow for high-performance electronics in displays.
Integrated Circuits: Research is ongoing into the use of CIGS in advanced semiconductor devices, including integrated circuits where its properties can be leveraged for improved performance.
Electrochemical Devices
Battery Technology: CIGS is explored in the development of advanced battery technologies. Its properties can be utilized to enhance the performance of batteries, particularly in high-efficiency energy storage applications.
Material Science and Coatings
Protective Coatings: CIGS can be used in various protective coatings due to its chemical stability and resistance to corrosion. These coatings can be applied to surfaces that require enhanced durability and resistance to environmental factors.
Nanocomposites: CIGS nanoparticles can be incorporated into nanocomposites to improve mechanical, electrical, or optical properties. This can be useful in developing advanced materials for various industrial applications.
Research and Development
Material Properties: CIGS is widely studied for its unique material properties, including its bandgap tuning, light absorption characteristics, and stability. Research into CIGS can lead to innovations in photovoltaic technologies and other semiconductor applications.