| COOH Functionalized Short MWCNTs | |
| Product No | NRE-35003 |
| CAS No. | NA |
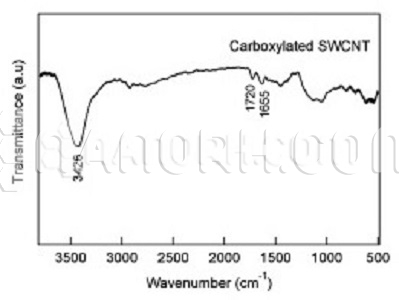
| Purity | Carbon nanotubes > 95wt% |
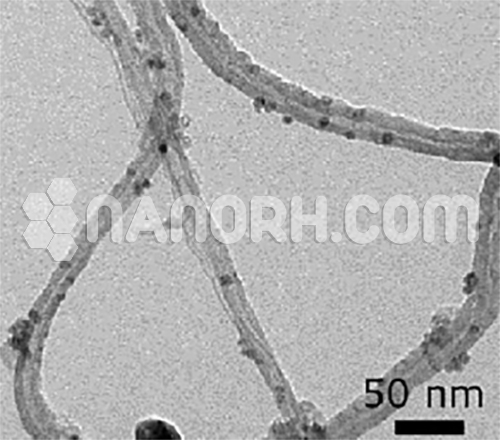
| Average Diameter | 50-80 nm |
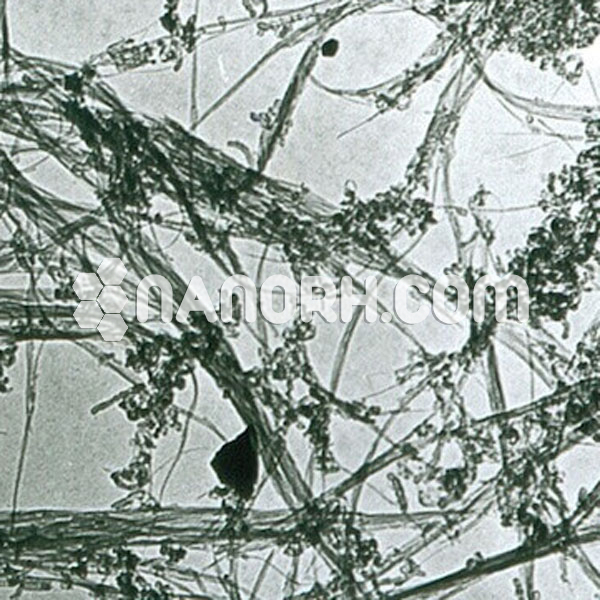
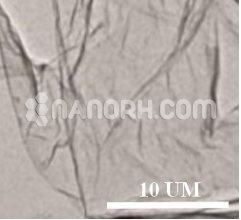
| Average Length | 0.5-2 um (TEM) |
| Special Surface Area(SSA) | >40m2/g(BET) |
| Tap Density | 0.18g/cm3 |
| True Density | 2.1g/cm3 |
| Electric Conductivity | > 100 S/cm |
COOH Functionalized Short MWCNTs
Applications
Nanocomposites and Polymer Reinforcement
Enhanced Mechanical and Electrical Properties: COOH-functionalized short MWCNTs are frequently incorporated into polymer matrices to create nanocomposites. The introduction of carboxyl groups improves the interaction between MWCNTs and the polymer, resulting in better dispersion, stronger interfacial bonding, and enhanced mechanical properties, such as increased strength and toughness.
Applications: These nanocomposites are used in the automotive, aerospace, and construction industries, as well as in electronics, where their high conductivity and mechanical strength are highly valued.
Energy Storage Devices
Supercapacitors and Batteries: The carboxyl groups on MWCNTs enhance their interaction with other materials, such as electrodes in supercapacitors and batteries. COOH-functionalized MWCNTs increase the electrical conductivity, surface area, and stability of the electrodes, leading to improved performance in energy storage devices. These nanotubes also facilitate the efficient transport of charge carriers, improving the overall efficiency of devices like lithium-ion batteries and supercapacitors.
Fuel Cells: COOH-functionalized MWCNTs can serve as catalyst supports in fuel cells, enhancing the performance of the catalytic reaction due to their high surface area and the ability to anchor metal nanoparticles effectively.
Biomedical Applications
Drug Delivery: Due to their biocompatibility and ability to functionalize with biological molecules, COOH-functionalized short MWCNTs are explored for use in drug delivery systems. The carboxyl groups can be used to attach drugs, proteins, or targeting agents, enabling controlled drug release to specific cells or tissues, especially for cancer treatment.