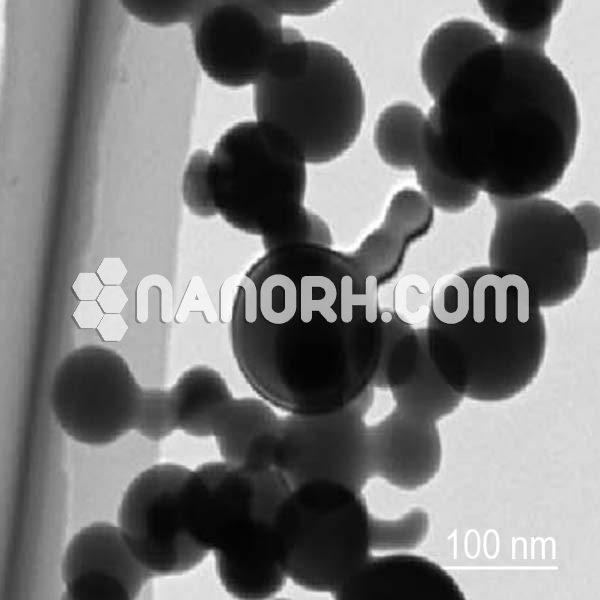
| Cobalt Phosphide Nanoparticles | |
| Product No | NRE-5065 |
| CAS No. | 12134-02-0 |
| Formula | Co2P |
| APS | <100 nm (Can be Customized) |
| Purity | 99.9% |
| Color | Gray |
| Molecular Weight | 148.84 g/mol |
| Density | 6.4 g/cm3 |
| Melting Point | 1386 °C |
| Boiling Point | NA |
Cobalt Phosphide Nanoparticles
Cobalt phosphide nanoparticles is an inorganic compound formed by cobalt and phosphorus. At the nanoscale, cobalt phosphide nanoparticles exhibit unique properties, such as high surface area, enhanced chemical reactivity, magnetic behavior, and improved electrical conductivity. These nanoparticles have garnered attention in various fields such as catalysis, energy storage, and environmental applications, owing to their excellent catalytic activity, magnetic properties, and the ability to be easily tailored for specific purposes.
Key Properties
Catalytic Activity: Cobalt phosphide is known for its excellent catalytic properties, especially in reactions such as hydrogen evolution (for water splitting) and in the hydrogenation of organic compounds.
High Surface Area: The high surface area of enhances their reactivity, making them effective in catalytic applications and as adsorbents in various processes.
Electrical Conductivity: exhibit good electrical conductivity, which makes them suitable for use in electrochemical devices like batteries and supercapacitors.
Magnetic Properties: Cobalt is a ferromagnetic material, and at the nanoscale, can exhibit enhanced magnetic properties, making them valuable for magnetic applications.
Applications
Catalysis:
Hydrogen Evolution Reaction (HER): Cobalt phosphide nanoparticles are widely studied for their excellent performance in hydrogen evolution reactions (HER), which are a crucial part of water splitting for hydrogen production. Their high catalytic activity makes them a promising material for clean energy generation by producing hydrogen from water.
Electrocatalysis: In addition to HER, cobalt phosphide nanoparticles are also employed in other electrochemical reactions such as oxygen evolution reaction (OER), carbon dioxide reduction, and nitrogen fixation. Their catalytic properties improve the efficiency of electrochemical processes, which are important for energy conversion and storage technologies.
Hydrogenation Reactions: Cobalt phosphide is an effective catalyst for hydrogenation reactions, which involve adding hydrogen atoms to unsaturated organic molecules. This is valuable in industries such as petrochemical refining, pharmaceuticals, and fine chemical production.
Energy Storage:
Batteries: Due to their good electrical conductivity, cobalt phosphide nanoparticles are being explored for use as anode materials in lithium-ion batteries (LIBs) and sodium-ion batteries (SIBs). They enhance the capacity and cycling stability of these batteries, which are widely used in consumer electronics, electric vehicles, and renewable energy storage.
Supercapacitors: Cobalt phosphide nanoparticles can also be used in the fabrication of supercapacitors, which store energy through electrostatic charge accumulation. Their high surface area and conductivity improve the energy density and charge-discharge efficiency of supercapacitors, making them suitable for high-power applications like electric vehicles and backup power systems.
Batteries for Renewable Energy: The nanoparticles’ ability to facilitate efficient charge/discharge cycles makes them useful in energy storage systems linked to renewable energy sources such as solar and wind power.
Magnetic Applications:
Magnetic Nanoparticles: Cobalt phosphide nanoparticles exhibit magnetic properties, and when used in magnetic materials, they can improve performance in devices such as magnetic storage systems and data storage. Their nanoscale size and magnetic properties make them attractive for high-density storage applications, sensors, and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) technologies.