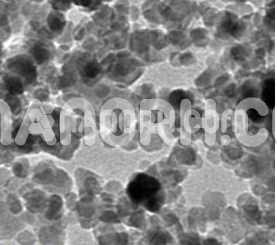
| Cerium Carbonate Nanoparticles | |
| Product No | NRE-5053 |
| CAS | 54451-25-1 |
| Purity | 99.9% |
| Formula | Ce2(CO3)3. xH2O |
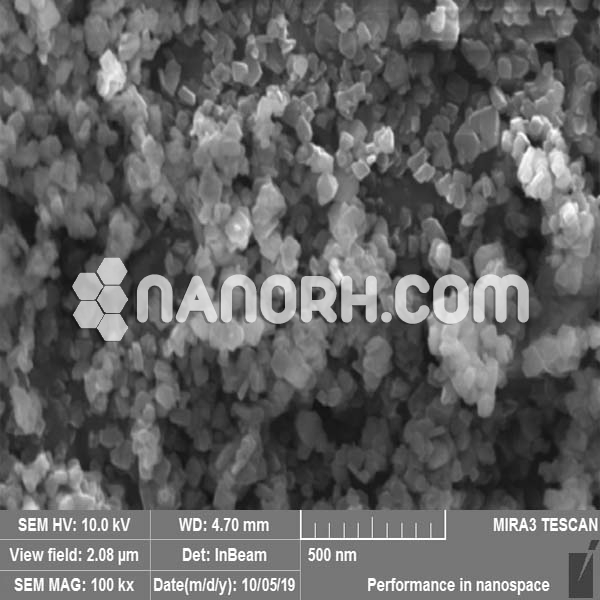
| APS | <100 nm (can be customized) |
| Color | White |
| Molecular Weight | 460.27 g/mol |
| Density | NA |
| Melting Point | NA |
| Boiling Point | NA |
Cerium Carbonate Nanoparticles
Cerium carbonate nanoparticles is an inorganic compound that combines cerium, a rare earth element, with carbonate ions. When reduced to the nanoscale, cerium carbonate exhibits unique properties that make it useful in a variety of scientific and industrial applications.
Applications:
Biomedical and Pharmaceutical Applications:
Antioxidant and Free Radical Scavenging: Cerium carbonate nanoparticles are studied for their antioxidant properties in biomedical applications. These nanoparticles can neutralize harmful free radicals (ROS) in the body, which are associated with aging and diseases like Alzheimer’s disease and Parkinson’s disease. They are explored for use in anti-aging products and in therapies to mitigate oxidative stress.
Drug Delivery: Due to their small size and biocompatibility, cerium carbonate nanoparticles have potential as drug delivery carriers. They can be functionalized to carry therapeutic drugs to targeted areas in the body, improving the efficacy of treatments for diseases like cancer, inflammatory disorders, and neurological diseases.
Imaging and Diagnostics: The optical properties of cerium carbonate nanoparticles enable their use in imaging applications, such as fluorescence imaging. Their ability to emit light when exposed to certain wavelengths makes them useful in cell imaging and diagnostic sensing.
Catalysis:
Environmental Catalysis: Cerium carbonate nanoparticles have shown promise in catalyzing environmental reactions, such as CO₂ reduction, NOx reduction, and wastewater treatment. Their redox properties allow them to be used in processes that require the oxidation or reduction of pollutants. For example, they are studied for catalytic converters in vehicles and industrial processes that aim to reduce harmful emissions.
Organic Synthesis: The catalytic properties of are also explored in organic chemistry for applications such as hydrogenation, oxidation reactions, and dehydrogenation. They are used as catalysts or catalyst supports to accelerate reactions in synthesis of chemicals and pharmaceuticals.
Environmental Remediation:
Heavy Metal Ion Adsorption: can be used for the removal of heavy metal ions like lead, cadmium, and arsenic from water or soil. The high surface area of the nanoparticles allows them to adsorb these pollutants efficiently, making them useful in environmental cleanup applications, such as water purification or soil decontamination.