| Calcium Carbide Nanoparticles | |
| Product No | NRE-5283 |
| CAS | 75-20-7 |
| Purity | 99.9% |
| Formula | CaC2 |
| APS | <100 nm (can be customized) |
| Color | White |
| Molecular Weight | 64.1 g/mol |
| Density | 2.22 g/cm3 |
| Melting Point | 2160 °C |
| Boiling Point | 2300 °C |
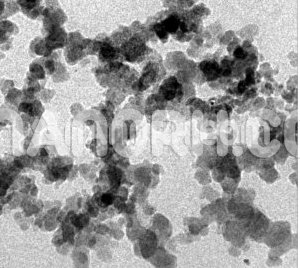
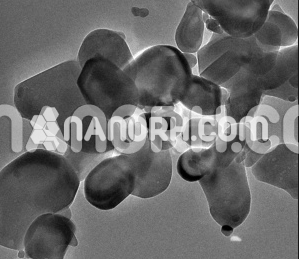
Calcium Carbide Nanoparticles
Introduction
Calcium carbide is a compound formed by the combination of calcium (Ca) and carbon (C). In its traditional form, it exists as a greyish solid, but when synthesized at the nanoscale, its properties are significantly altered.
Properties
Increased Surface Area:
One of the most important properties of CaC₂ nanoparticles is their high surface area to volume ratio, which enhances their chemical reactivity and makes them more efficient for use in catalysis and chemical reactions.
Reactivity with Water:
Calcium carbide reacts vigorously with water to produce acetylene gas (C₂H₂) and calcium hydroxide (Ca(OH)₂). The enhanced surface area of CaC₂ nanoparticles increases the speed and efficiency of this reaction, making them useful in applications that require rapid production of acetylene, such as in synthetic chemistry.
Applications
Synthesis of Acetylene Gas:
CaC₂ reacts with water to release acetylene (C₂H₂), a crucial component in the chemical industry for the production of various organic compounds and as a fuel. When used in nanoparticle form, CaC₂ nanoparticles can increase the reaction rate, providing a more efficient process for acetylene production. This reaction is also used in welding and cutting applications where acetylene is employed as a fuel gas.
Catalysis and Chemical Reactions:
Due to their high surface area and reactive nature, CaC₂ nanoparticles are excellent catalysts for various chemical processes. They can be used in the synthesis of organic compounds, including acetylene derivatives, and in polymerization reactions. These nanoparticles also find application in the conversion of methane into valuable hydrocarbons or synthetic fuels via catalytic processes.
They are also used in the reduction and hydrogenation of certain organic compounds in the pharmaceutical industry.