Cadmium Sulfide Powder / CdS Powder (CdS, Super Grade, 12um, 99.99%)
Cadmium sulfide is the inorganic compound with the recipe CdS. Cadmium sulfide is a yellow strong. It happens in nature with two distinctive precious stone structures as the uncommon minerals greenockite
| Cadmium Sulfide Nanoparticles | |
| Product No | NRE-5039 |
| CAS No. | 1306-23-6 |
| Formula | CdS |
| APS | <100nm (Can be Customized) |
| Purity | 99.9% |
| Color | Yellow-Orange |
| Molecular Weight | 144.47 g/mol |
| Density | 4.82 g/cm³ |
| Melting Point | 1750 °C |
| Boiling Point | 980 °C |
Cadmium Sulfide Powder / CdS Powder
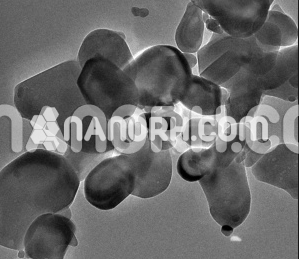
Cadmium Sulfide nanoparticles is a chemical compound composed of cadmium (Cd) and sulfur (S). It is a yellow or pale orange solid that is widely recognized for its significant optical, electronic, and semiconducting properties. Over the years, CdS powder has garnered interest across various scientific and industrial fields due to its unique properties, which arise from its crystalline structure, band gap, and high surface area when processed at the micron or nanometer scale.
CdS powder, in its bulk form, typically exists as a yellow pigment and is a widely used material in the production of pigments, photovoltaic devices, photocatalysts, and optical materials.
Properties:
Band Gap:
Cadmium sulfide nanoparticles has a wide band gap (~2.4 eV), which allows it to efficiently absorb visible light and is highly responsive to sunlight. This property is crucial for its use in solar cells and photovoltaic applications, where light absorption is key to converting light energy into electrical energy.
Photoluminescence:
CdS powder is known for its bright photoluminescence, emitting a yellow or greenish light when excited. The quantum confinement effect in nanoparticles further enhances these properties, allowing for tunable emissions that make CdS ideal for applications in biolabeling, fluorescent imaging, and light-emitting devices.
Semiconducting Nature:
CdS is classified as a n-type semiconductor, meaning it has a high concentration of free electrons in its structure. This makes it useful in a variety of electronic and optoelectronic applications, particularly in devices like photodetectors and light sensors.
Toxicity:
One of the critical considerations for CdS powder is the toxicity of cadmium, a heavy metal that can be hazardous to both human health and the environment. The toxicity of cadmium has led to regulations regarding its use, especially in applications involving biological exposure or environmental release. As a result, researchers have focused on finding safe alternatives to CdS, while ensuring that its benefits in technological applications remain harnessed.