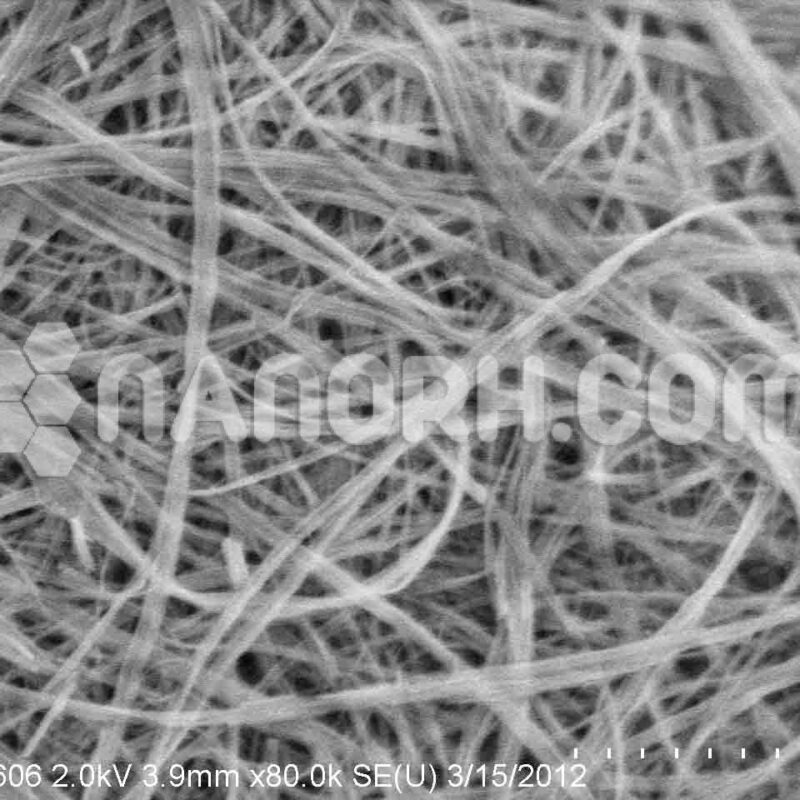
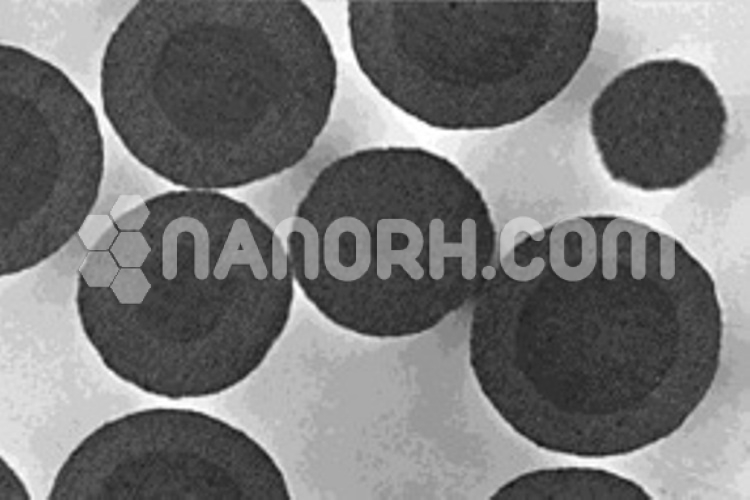
| Cadmium Selenium/ Silica Core Shell Nanoparticles | |
| Product No | NRE-16006 |
| CAS No. | NA |
| Formula | CdSe/SiO |
| APS | <100nm (can be customized) |
| Shape | Spherical |
| Purity | 99.9% |
| Core | Cadmium Sulfide |
| Shell | Silica |
| Melting Point | NA |
| Boiling Point | NA |
Cadmium Selenium/ Silica Core-Shell Nanoparticles
Cadmium selenium/ silica Core-shell Nanoparticles due to their unique size-dependent properties, have revolutionized a wide array of fields, including materials science, medicine, optoelectronics, and catalysis. Among the many types of nanoparticles, core-shell nanoparticles—where one material forms the core and another material coats the core as a shell—are particularly valuable due to their ability to combine the distinct properties of each component, leading to enhanced functionality.
Optoelectronic Applications
Light-Emitting Diodes (LEDs): CdSe is well-known for its tunable photoluminescence, making it suitable for use in LEDs and other optoelectronic devices. By embedding CdSe nanoparticles into a device structure, their light emission properties can be engineered to produce specific colors or wavelengths of light. The silica shell improves the long-term stability of these devices, making them more durable and efficient.
Solar Cells: The excellent light-absorbing properties of CdSe, coupled with the protective and stabilizing role of the silica shell, make CdSe@SiO₂ core-shell nanoparticles suitable for integration into solar cell devices. The quantum dots can enhance the efficiency of photovoltaic devices by improving light absorption and charge transport.
Environmental Applications
Environmental Remediation: CdSe@SiO₂ core-shell nanoparticles can be used in environmental applications like water purification or pollutant detection. The unique optical properties of the core material can be harnessed for the detection of harmful substances, while the silica shell provides stability and ease of handling in environmental conditions.
- Challenges and Future Directions
While CdSe@SiO₂ core-shell nanoparticles have demonstrated considerable promise in numerous applications, several challenges remain:
Toxicity of Cadmium: Despite the protective role of the silica shell, the presence of cadmium in the core still poses concerns in biological systems, especially in long-term exposure scenarios. Research into cadmium-free alternatives, such as zinc selenide (ZnSe) or cadmium-free quantum dots, is ongoing to mitigate these concerns.
Synthesis Control: Achieving uniform, reproducible, and scalable synthesis of high-quality CdSe@SiO₂ nanoparticles with controlled size, shape, and shell thickness remains a challenge. Advances in synthesis techniques and quality control are needed for broader commercial applications.
Surface Functionalization: While silica offers a robust platform for surface modification, further research into optimizing the functionalization of the silica shell with targeting agents, drugs, or other molecules is necessary to fully exploit the potential of these nanoparticles in drug delivery, biosensing, and other biomedical applications.
Catalysis
CdSe quantum dots can also be used in catalysis, especially in photocatalysis and energy conversion applications. The silica shell provides a stable matrix for the CdSe core, facilitating the generation of charge carriers upon light exposure, which can drive catalytic reactions. The silica shell also helps in stabilizing the core and preventing unwanted side reactions, making these core-shell nanoparticles effective in processes like hydrogen production, carbon dioxide reduction, or pollutant degradation.