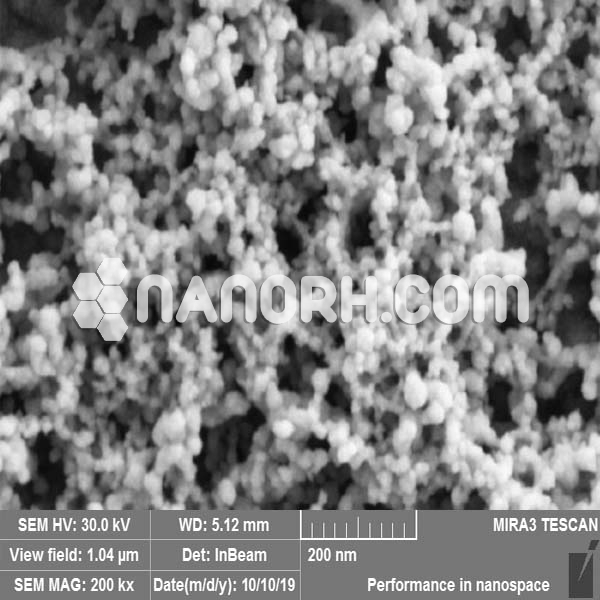
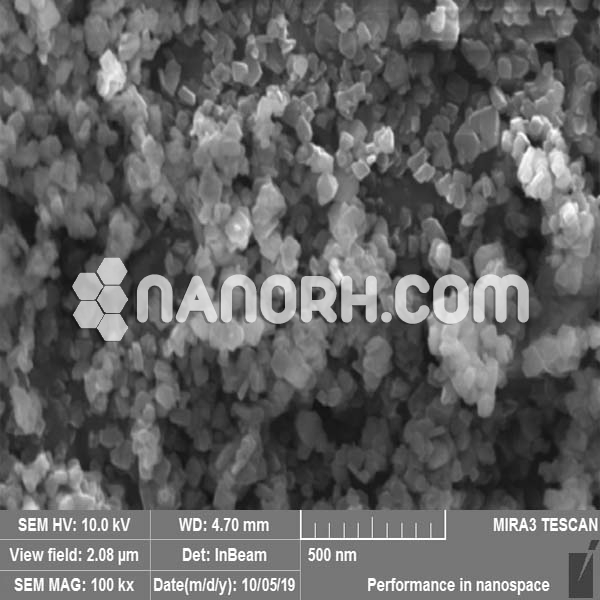
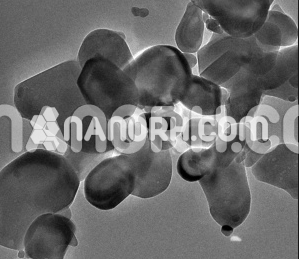
Bismuth Oxide Nanopowder / Nanoparticles (Bi2O3, 99.9%, 80nm)
Over 710 oC, liquefying bismuth oxide can disintegrate or break up metal oxides. The fundamental reason: the hardware business; weight touchy resistors; Capacitance of major doping materials; medication; counterfeit bone imaging; glass; Bismuth oxide in earthenware production can build the file of refraction of glass and essentially enhance the execution of clay material. It is the best substitute of “Lead Glaze”.
| Bismuth Oxide Nanoparticles | |
| Product No | NRE-3007 |
| CAS No. | 1304-76-3 |
| Formula | Bi2O3 |
| APS | <100nm (Can be Customized) |
| Purity | 99.9% |
| Color | yellow |
| Molecular Weight | 465.96 g/mol |
| Density | 8.9 g/cm3 |
| Melting Point | 817°C |
| Boiling Point | 1890°C |
Bismuth Oxide Nanoparticles (Bi2O3) Applications:
Over 710 oC, liquefying bismuth oxide can disintegrate or break up metal oxides. The fundamental reason: the hardware business; weight touchy resistors; Capacitance of major doping materials; medication; counterfeit bone imaging; glass; Bismuth oxide in earthenware production can build the file of refraction of glass and essentially enhance the execution of clay material.
Applications
Catalysis:
Catalysts for Oxidation Reactions: Bi₂O₃ nanoparticles are widely used as catalysts in oxidation reactions, such as the oxidation of organic compounds and in the production of fine chemicals. They are effective for environmentally friendly catalytic processes due to their ability to promote oxidation reactions with minimal energy consumption.
Fuel Cells: Bismuth oxide nanoparticles are being investigated for use in solid oxide fuel cells (SOFCs). Their role as a catalyst improves the efficiency of fuel cells by enhancing the electrochemical reactions involved in energy conversion.
Electronics and Semiconductor Devices:
Electrodes and Semiconductors: Bi₂O₃ nanoparticles have been used in the development of electrode materials for semiconductor devices. Their ability to conduct electricity under certain conditions makes them useful in the production of high-performance transistors, capacitors, and diodes.
Photocatalysis: Bismuth oxide nanoparticles have shown potential in photocatalysis, where they are used to accelerate chemical reactions when exposed to light. This has applications in solar energy conversion, water splitting, and environmental remediation.
Sensing and Detection:
Gas Sensors: Bi₂O₃ nanoparticles are used as gas sensors for detecting gases such as nitrogen dioxide (NO₂), carbon monoxide (CO), and ethanol. Their sensitivity to changes in the surrounding atmosphere makes them useful in environmental monitoring and industrial safety applications.
Biosensors: The surface reactivity and biocompatibility of Bi₂O₃ nanoparticles are being explored for biosensor applications, where they can help detect biological markers and pathogens, aiding in healthcare diagnostics and environmental monitoring.
Energy Storage:
Supercapacitors: Bi₂O₃ nanoparticles are considered for use in supercapacitors, which store electrical energy and provide high power output for applications such as electric vehicles, renewable energy systems, and portable electronics.
Lithium-Ion Batteries: Bismuth oxide has been studied as a potential anode material for lithium-ion batteries due to its high surface area and favorable electrochemical properties. This can lead to the development of more efficient and durable batteries.