| Bismuth Iodide Nanoparticles | |
| Product No | NRE-5026 |
| CAS | 7787-64-6 |
| Purity | 99.9% |
| Molecular Formula | BiI3 |
| Molecular Weight | 589.69 g/mol |
| Color | greenish-black |
| Density | 5.78 g/cm3 |
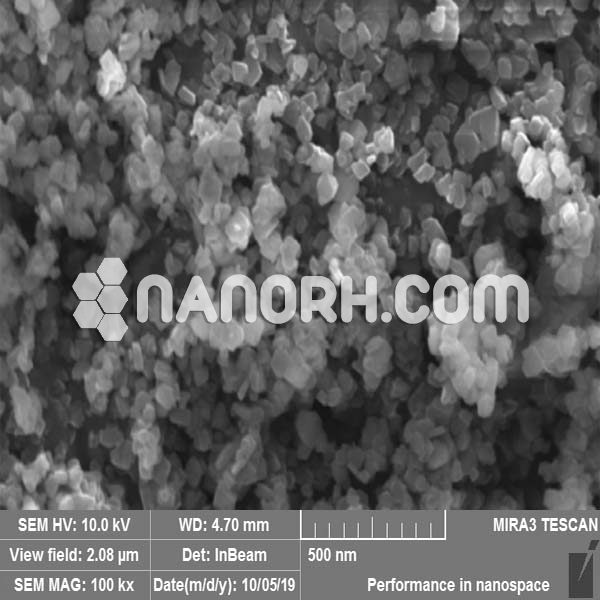
| APS | <100 nm(can be customized) |
| Melting Point | 408.6° C |
| Boiling Point | 542° C |
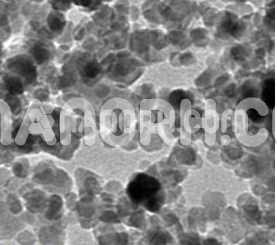
Bismuth Iodide Nanoparticles
Bismuth Iodide (BiI₃) is an inorganic compound formed by bismuth and iodine, typically appearing as a yellow crystalline solid. At the nanoscale, bismuth iodide forms nanoparticles (BiI₃ NPs) that exhibit unique physical and chemical properties compared to the bulk material. These nanoparticles generally range in size from 1 to 100 nanometers and possess enhanced surface area, optical properties, electronic behavior, and reactivity.
Properties
Layered Crystal Structure:
Bismuth iodide nanoparticles adopt a layered crystal structure, similar to graphene and other 2D materials, which is essential for their unique electronic and optical properties. This allows for easy exfoliation into thin layers, enabling the creation of nanostructured films for use in optical devices and energy applications.
Photovoltaic Properties:
BiI₃ nanoparticles have shown photovoltaic properties, meaning they can absorb light and convert it into electrical energy. This makes them valuable for use in solar cells and photoelectric devices.
Applications
Photovoltaic and Solar Cells:
Bismuth iodide nanoparticles are being explored as a material for solar cells due to their photovoltaic properties. The ability of BiI₃ to absorb light and convert it into electricity makes it a potential alternative to traditional silicon-based solar cells, offering the possibility of low-cost, flexible, and lightweight energy-harvesting devices.
Photocatalysis:
BiI₃ nanoparticles show great promise as photocatalysts, particularly in solar-driven chemical reactions such as water splitting (for hydrogen production) and degradation of organic pollutants. Their ability to absorb UV and visible light makes them effective for environmental cleanup and energy conversion applications.
Bismuth iodide is also being explored for carbon dioxide reduction, where it can act as a photocatalyst to convert CO₂ into useful organic compounds.
Photodetectors and Optoelectronic Devices:
Bismuth iodide nanoparticles have excellent light absorption properties, making them suitable for photodetectors in optical communication systems and image sensors. Their high photovoltaic efficiency can also be leveraged in optoelectronic devices, such as light sensors, photo-switches, and displays.
Light-emitting diodes (LEDs) and laser technologies also benefit from the strong luminescence of BiI₃ nanoparticles, especially in applications requiring bright, stable light emission.