| Barium Fluoride Nanopowder | |
| Product No | NRE-5020 |
| CAS No. | 7787-32-8 |
| Formula | BaF2 |
| APS | <100nm (Can be Customized) |
| Purity | 99.9% |
| Color | White |
| Molecular Weight | 175.34 g/mol |
| Density | 4.893 g/cm³ |
| Melting Point | 1368 °C |
| Boiling Point | 2260 °C |
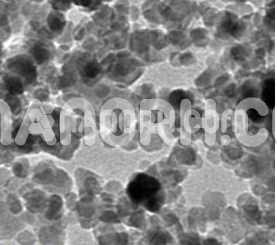
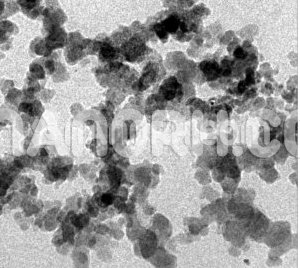
Barium Fluoride Nanopowder
Barium Fluoride is an inorganic compound consisting of barium and fluorine, primarily recognized for its optical and chemical properties. In its bulk form, barium fluoride is a white crystalline solid, but when reduced to nanopowder form, it exhibits enhanced physical and chemical characteristics such as increased surface area, reactivity, and dispersion properties. The nanopowder of barium fluoride typically consists of particles with sizes ranging from 1 to 100 nanometers, which contributes to its superior performance in a variety of applications compared to its bulk form.
Applications
Optical Applications
Infrared Optics: Barium fluoride is widely used in infrared optical systems due to its low refractive index and high transmission in the infrared region (1.5 to 8 μm). Barium fluoride nanopowder is particularly useful in the manufacture of infrared lenses, windows, and optical fibers used in infrared imaging, thermal imaging, and spectroscopic analysis.
Laser Technology: Barium fluoride nanopowder is used in laser optics and laser window applications due to its high optical transparency in the infrared region. It is also used in laser crystals for high-power lasers, enhancing the efficiency and output of laser systems used in scientific and industrial applications.
Electronics and Sensors
Electrochemical Devices: BaF2 can be used in electrochemical sensors and supercapacitors due to its enhanced ionic conductivity. Its high surface area makes it an excellent candidate for use in energy storage devices that require fast charging and high energy density.
Piezoelectric Sensors: Due to its specific electronic properties at the nanoscale, has been explored in the development of piezoelectric sensors for measuring pressure, acceleration, and force. These sensors are useful in a wide range of applications, including medical diagnostics, industrial monitoring, and automotive systems.