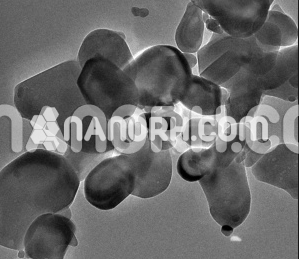
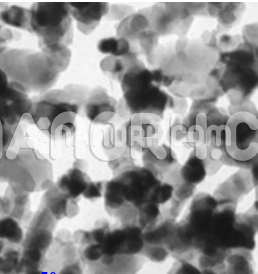
| Barium Carbonate Nanoparticles | |
| Product No | NRE-5018 |
| CAS No. | 513-77-9 |
| Formula | BaCO3 |
| APS | <100nm (Can be Customized) |
| Purity | 99.9% |
| Color | White |
| Molecular Weight | 197.34 g/mol |
| Density | 4.286 g/cm3 |
| Melting Point | 811 °C |
| Boiling Point | 1450 °C |
Barium Carbonate Medicine Powder
Applications of Barium Carbonate Medicine Powder
Radiological Applications
Contrast Medium for X-ray Imaging: One of the most common uses of barium carbonate powder in medicine is in the form of a contrast agent for X-ray imaging of the gastrointestinal (GI) tract. Barium sulfate, a related compound, is often used for barium meals, barium enemas, and barium swallow studies. While barium carbonate itself isn’t typically ingested or used directly for imaging, it is a precursor in the synthesis of barium sulfate, which is then used as the contrast medium.
Treatment of Certain Poisonings
Barium Poisoning: Although barium carbonate itself is toxic, in certain cases of barium toxicity or poisoning, barium carbonate may be used as part of an antidote treatment, especially if a person has ingested large quantities of barium salts. This is a specialized application, and treatment often involves the administration of medical charcoal, which can absorb the barium compound in the digestive tract.
Industrial and Therapeutic Use
Use in the Manufacture of Barium Sulfate: Although barium sulfate is more commonly used as a contrast agent for imaging, barium carbonate is an intermediate in the synthesis of barium sulfate. It is used to produce barium sulfate for medical applications, including its use in diagnostic imaging.
Pharmaceutical Applications
As a Precursor in Drug Formulation: While barium carbonate itself is rarely used directly in pharmaceuticals, its precursors (such as barium sulfate) are often used in drug formulations, particularly as radio-opaque agents in diagnostic procedures. Additionally, it is used in the manufacture of other barium-based compounds, which are then applied in medical imaging and diagnostic procedures.
Safety and Toxicity Concerns
Despite its usefulness in certain medical applications, barium carbonate is highly toxic if ingested or inhaled in large quantities. Overdose can result in severe side effects, including:
Gastrointestinal irritation
Nausea and vomiting
Respiratory issues
Cardiac arrhythmias.