3D Printing Metal Powder
The main application of 3D printing metal powder;
Aerospace
Molds
Automotive
Medical instruments
Military industry
| Product No. | Metal Powder | Composition (%) | O (%) | A.D.g/cm3 | Particle Size |
| NRE-60004 | NRE-Sn | Sn 99.95 | 0.05-0.08 | 3.5-5.0 | 15-45um, 45-106um, D50 10-15um, D50 1-2um, D50 0.5-1um. |
| NRE-Cu | Cu 99.5 | ||||
| NRE-Ni | Ni 99.8 | ||||
| NRE-WCCo | WC 92-94 Co 6-8 | ||||
| NRE-CuAlNiFe | Al 10 Ni 5 Fe 5 | 3.5-5.0 | |||
| NRE-Ag | Ag 99.9 | 3.5-5.0 |
3D Printing Metal Powder
Introduction
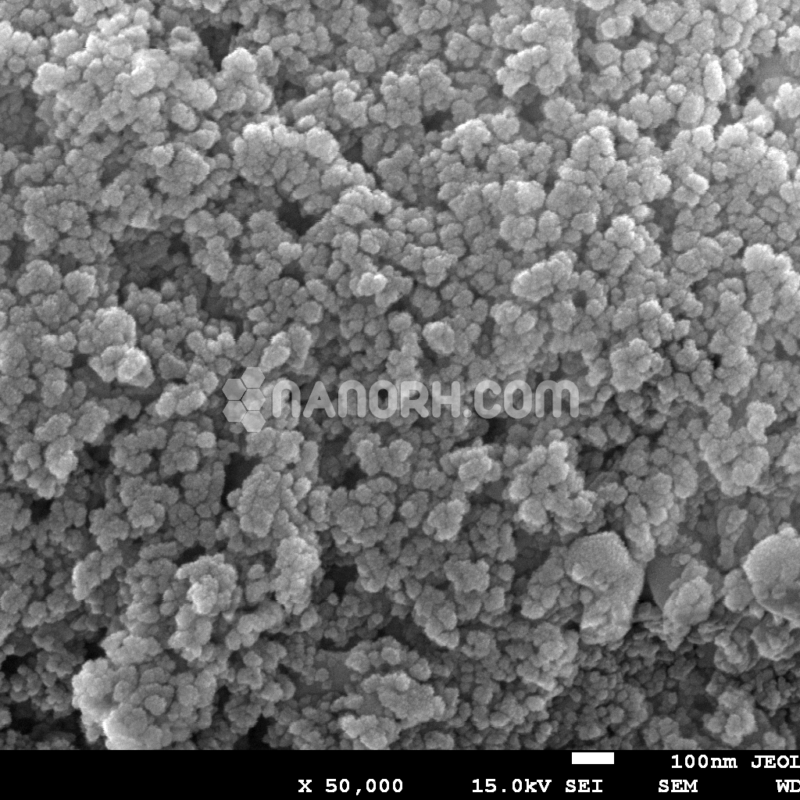
3D printing metal powders are fine, powdered materials used in additive manufacturing (AM) or 3D printing processes to create metal parts layer by layer. These powders are produced from a range of metal alloys, and they play a crucial role in industries requiring high precision and customized, complex geometries. Some of the most common metal powders used in 3D printing include materials like titanium (Ti), stainless steel (SS), aluminum (Al), nickel alloys, tungsten, copper (Cu), magnesium alloys, and cobalt-chrome.
The production of metal powders for 3D printing typically involves methods such as gas atomization, water atomization, or plasma atomization. These techniques involve melting metal and spraying it through a nozzle to form small droplets, which solidify into uniform spherical particles that are ideal for AM applications.
Features of 3D Printing Metal Powder
Particle Size and Distribution:
Metal powders used in 3D printing have a specific particle size range, typically between 20 to 100 microns, depending on the printing process. The uniformity of the particle size distribution is critical for good flowability, which ensures consistent layer deposition and optimal results during the printing process.
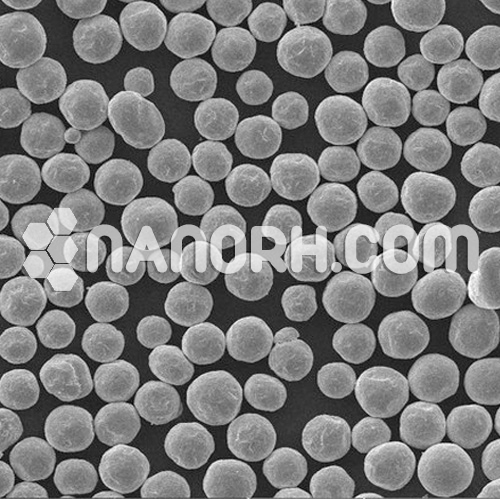
Spherical Morphology:
Most metal powders used in 3D printing are spherical in shape. This spherical morphology improves the flowability of the powder, facilitating smooth feeding into the printer’s build chamber. Spherical particles allow for high packing density, which results in more efficient use of the material and helps achieve better mechanical properties in the final printed part.
High Purity and Consistency:
The quality of the metal powder must be of high purity to avoid defects in the printed parts. The powder must also have consistent composition, as fluctuations in material properties could lead to issues such as warping, porosity, or structural weaknesses in the printed component.