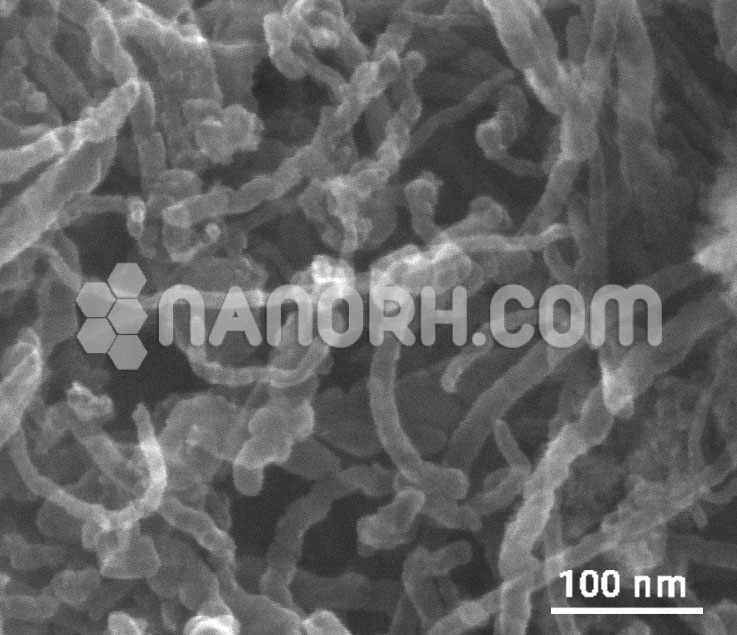
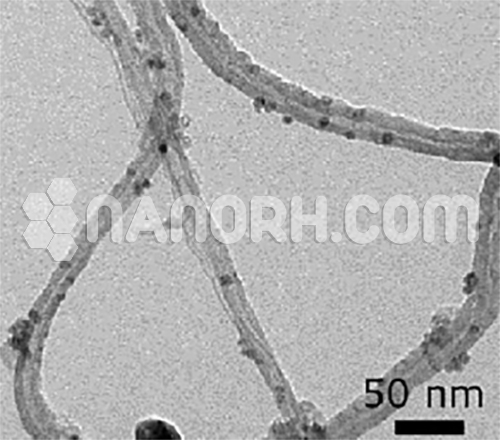
Palladium coated Carbon Nanotubes (Pd/CNT)
| Palladium Coated Carbon Nanotubes | |
| Product No | NRE-42005 |
| CAS No. | 7440-05-3/308068-56-6 |
| Outer Diameter | 35-50 nm |
| Inner Diameter | 5-25nm |
| Average Length | 10-20um |
| True Density | 2.1 g/cm3 |
| Electric Conductivity | > 100 S/cm |
| Metal Percentage | 2-5% (can be Customized) |
Palladium Coated Carbon Nanotubes– exhibit outstanding chemical activity due to their large active surface area and unique crystallographic surface structure.
Palladium Coated Carbon Nanotubes – CNTs decorated with metal nanoparticles (NPs) like Silver nanoparticles, Gold nanoparticles, Nickel nanoparticles, copper nanoparticles, Magnesium nanoparticles, palladium nanoparticles, platinum nanoparticles, exhibit outstanding chemical activity due to their large active surface area and unique crystallographic surface structure.
Applications
Catalysis and Chemical Reactions
Hydrogenation and Dehydrogenation Reactions: Palladium is widely used as a catalyst in hydrogenation and dehydrogenation reactions, which are common in the production of fine chemicals, pharmaceuticals, and petrochemicals. Pd-CNTs enhance these processes by providing more active sites and improving the efficiency of the reactions, such as in the hydrogenation of unsaturated hydrocarbons or the dehydrogenation of alkanes.
Cross-Coupling Reactions: Palladium is also a key catalyst in cross-coupling reactions like the Suzuki and Heck reactions, which are important for the synthesis of complex organic molecules. Pd-CNTs can improve the efficiency of these reactions by enhancing the palladium’s activity and stability, making them ideal for use in chemical synthesis and pharmaceutical manufacturing.
Carbon Monoxide (CO) Oxidation: Palladium is known for its ability to catalyze the oxidation of carbon monoxide (CO), a reaction that is important in environmental pollution control and automotive exhaust systems. Pd-CNTs can be used in CO oxidation catalysts to reduce CO emissions in industrial and automotive applications.
Energy Storage and Conversion
Fuel Cells: Palladium is a good catalyst for both the hydrogen oxidation reaction (HOR) and the oxygen reduction reaction (ORR) in fuel cells, making Pd-CNTs highly effective for use in hydrogen fuel cells. The high surface area of CNTs helps increase the catalyst’s effectiveness, improving the efficiency of fuel cells for power generation.
Hydrogen Storage: Pd-CNTs have also been studied for hydrogen storage applications, as palladium is known to absorb large amounts of hydrogen. The CNTs serve as a structural framework that improves the material’s capacity to store hydrogen, which can be released or used in fuel cells as needed.
Supercapacitors: Pd-CNTs can be used in supercapacitors, energy storage devices that store energy electrostatically. The combination of palladium’s conductivity and the high surface area of CNTs helps enhance the performance of supercapacitors, providing high power density and rapid charge/discharge cycles.