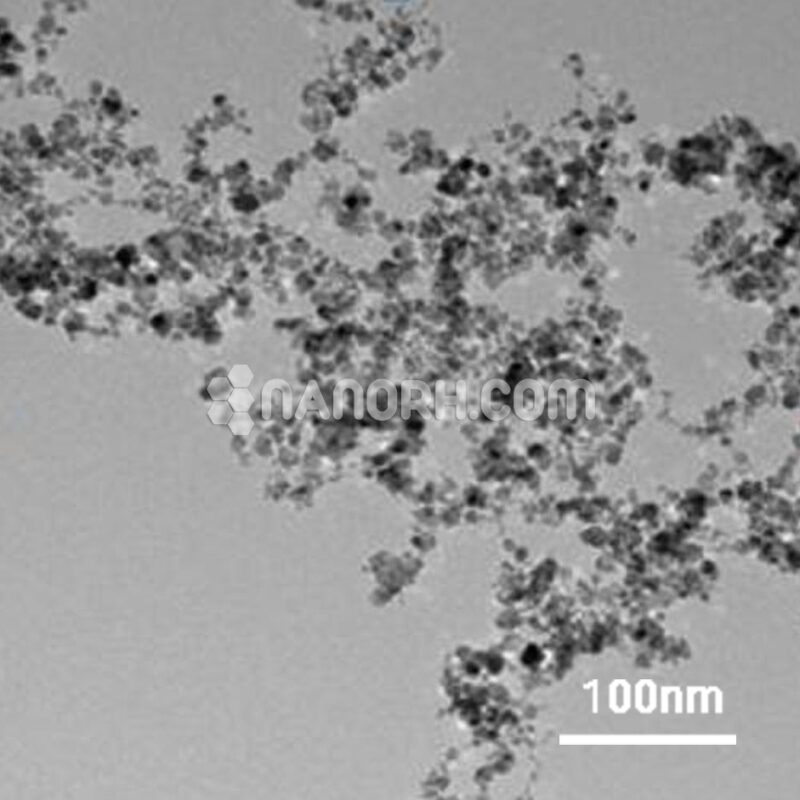
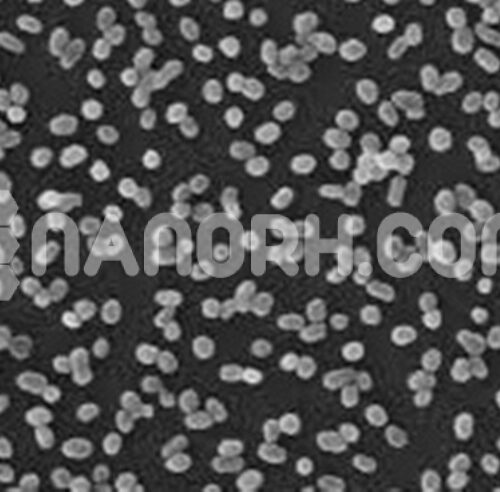
| Hafnium Powder / Hf Powder | |
| Product No | NRE-8022 |
| CAS No. | 7440-58-6 |
| Formula | Hf |
| Molecular Weight | 178.49 g/mol |
| APS | <40um(can be customized) |
| Purity | 99.9% |
| Color | Grey |
| Density | 13.31 g/cm3 |
| Melting Point | 2506 K (2233 °C, 4051 °F) |
| Boiling Point | 4876 K (4603 °C, 8317 °F) |
Hafnium Powder / Hf Powder
Hafnium is a chemical element with the symbol Hf and atomic number 72. It is a lustrous, silvery-gray, tetravalent transition metal, and its powder form has various applications in different fields. Here are some of the applications of hafnium powder:
Aerospace and Aviation: Hafnium is used in the aerospace industry, particularly in the manufacturing of jet and rocket engines. It has a high melting point, excellent heat resistance, and can withstand extreme temperatures, making it valuable for components in high-performance aircraft and spacecraft.
Plasma Cutting Tips: Hafnium is used in the production of plasma cutting tips. These tips are used in high-temperature cutting applications, such as in metalworking and welding. Hafnium tips can withstand the extreme heat generated during plasma cutting.
Electronics and Semiconductors: Hafnium dioxide (HfO2) is used as a high-k dielectric material in the production of advanced semiconductor devices, such as integrated circuits (ICs) and field-effect transistors (FETs). The use of hafnium-based materials helps reduce power consumption and improve the performance of electronic devices.
Alloys and Superalloys: Hafnium is used as an alloying element to improve the properties of various materials, including titanium and zirconium alloys. These hafnium-containing alloys are used in the aerospace industry, where strength, corrosion resistance, and heat resistance are critical.
Lighting: Hafnium is used in incandescent lamp filaments, helping to improve the efficiency and lifespan of these light sources.
X-ray Tubes: Hafnium is used as a target material in X-ray tubes for medical and industrial radiography. When bombarded with electrons, hafnium emits X-rays that are used for various imaging applications.
Neutron Absorption: Due to its high neutron-absorbing properties, hafnium is used in applications related to nuclear safety and nuclear physics experiments, helping to control nuclear reactions and reduce the risk of criticality accidents.
Catalysts: Hafnium compounds are used as catalysts in various chemical reactions, including polymerization and other industrial processes.
Optical Coatings: Hafnium oxide thin films are used in optical coatings, especially in interference filters and anti-reflective coatings on lenses and windows.