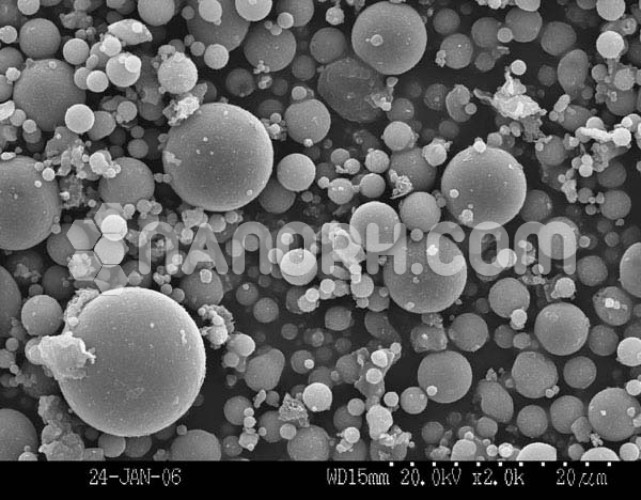
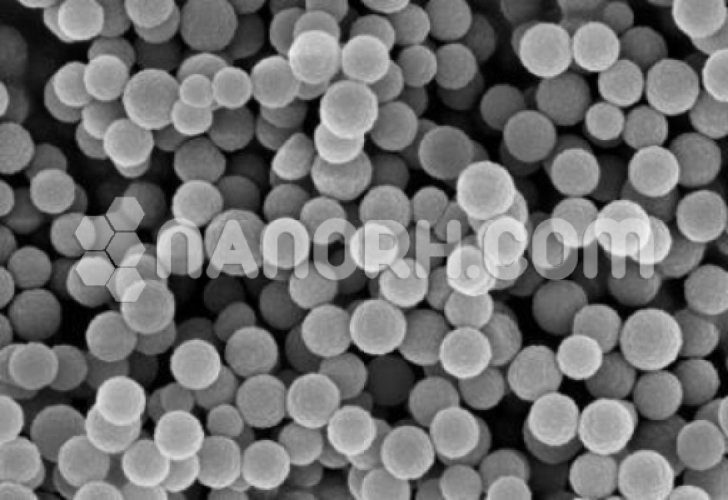
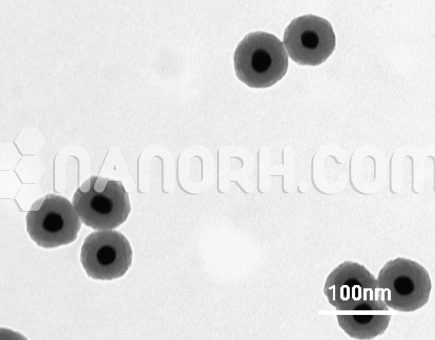
CdS/ PbS Core Shell Nanoparticles (CdS/PbS, 99.9%, APS: 80-100nm, Inorganic (Semiconductor) core/shell Nanoparticles)
| CdS/ PbS Core Shell Nanoparticles | |
| Product No | NRE-16021 |
| CAS No. | NA |
| Formula | CdS/PbS |
| APS | <100nm (can be customized) |
| Shape | Spherical |
| Purity | 99.9% |
| Core | Cadmium Selenium |
| Shell | Lead Sulfide |
| Appearance | Powder |
| Boiling Point | NA |
CdS/ PbS Core-Shell Nanoparticles
CdS/PbS core-shell nanoparticles combine the unique properties of cadmium sulfide (CdS) and lead sulfide (PbS), two semiconductor materials that exhibit distinct electronic, optical, and photocatalytic properties. These core-shell nanoparticles consist of a CdS core and a PbS shell, which together offer enhanced functionalities for a variety of applications in optoelectronics, photocatalysis, energy harvesting, and biosensing.
Applications
Photocatalysis and Solar Energy Conversion
Photocatalytic Water Splitting: CdS is an efficient photocatalyst for water splitting, and when combined with PbS, the CdS/PbS core-shell nanoparticle can exhibit enhanced solar-to-hydrogen conversion efficiency. The PbS shell extends the absorption spectrum into the infrared region, improving the overall photocatalytic efficiency under a broader range of sunlight.
Pollutant Degradation: The photocatalytic properties of CdS/ PbS core-shell nanoparticles make them effective in degrading organic pollutants, including dyes, pesticides, and industrial waste products, under UV or visible light. The enhanced absorption characteristics of the PbS shell further improve their effectiveness in environmental cleanup.
Solar Cells and Photovoltaic Devices
Quantum Dot Solar Cells: CdS is often used as a window material in quantum dot solar cells, and the PbS shell can improve the light absorption efficiency, particularly in the infrared region. The core-shell structure can also promote better charge separation and charge transport, enhancing the overall power conversion efficiency of solar cells.
Photovoltaic Devices: CdS/PbS nanoparticles can be incorporated into thin-film solar cells or photoelectrochemical cells, where their tunable optical properties make them highly efficient for light absorption and conversion into electrical energy.
Infrared Photodetectors
The PbS shell, with its narrow bandgap, is particularly sensitive to infrared (IR) radiation. CdS/PbS core-shell nanoparticles are thus highly suited for infrared photodetectors and night-vision devices, where they can absorb IR light and convert it into electrical signals. These nanoparticles could be used in applications such as thermal imaging, remote sensing, and infrared spectroscopy.
Biosensing and Bioimaging
Fluorescence and Luminescence: The photoluminescent properties of CdS combined with the infrared absorption capabilities of PbS enable these nanoparticles to be used in biosensing and bioimaging applications. CdS/PbS nanoparticles can be functionalized with specific biomolecules for targeted sensing of disease markers, such as cancer biomarkers or pathogens.
Quantum Dots for Imaging: The quantum dot properties of the nanoparticles enable high-resolution biological imaging, as they can be designed to emit in specific wavelengths based on the core-shell size and material composition.
Thermoelectric Devices
Thermoelectric Materials: Due to their narrow bandgap and charge transport properties, CdS/PbS core-shell nanoparticles are also being explored for use in thermoelectric devices that convert waste heat into electricity. The combination of high thermoelectric efficiency and infrared absorption makes them promising candidates for energy harvesting from low-grade heat sources.