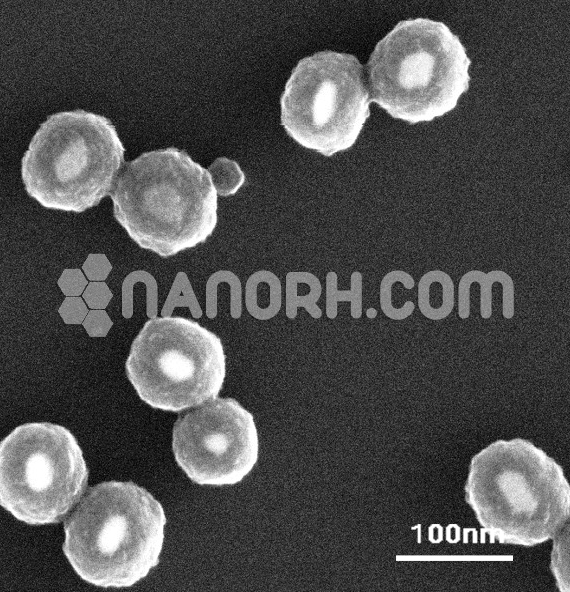
| Cadmium Sulfide/ Silver Core Shell Nanoparticles | |
| Product No | NRE-16010 |
| CAS No. | NA |
| Formula | CdS/ Ag |
| APS | <100nm (can be customized) |
| Shape | Spherical |
| Purity | 99.9% |
| Core | Cadmium Sulfide |
| Shell | Silver |
| Melting Point | NA |
| Boiling Point | NA |
Cadmium Sulfide/ Silver Core-Shell Nanoparticles
Core Composition: Cadmium Sulfide (CdS)
Cadmium sulfide (CdS) is a narrow-bandgap semiconductor with a bandgap of approximately 2.4 eV, which enables it to absorb light in the visible range. CdS has several significant applications due to its photonic and electronic properties:
Photoluminescence: CdS is widely used in quantum dots due to its size-tunable fluorescence, where the emission wavelength can be adjusted based on the particle size. This property makes CdS suitable for biological imaging and sensing applications.
However, CdS nanoparticles often suffer from rapid recombination of charge carriers and toxicity (due to the presence of cadmium), which can limit their use, especially in biological and environmental applications.
- Shell Composition: Silver (Ag)
Silver (Ag) is a noble metal known for its plasmonic properties, which enable it to interact strongly with light, especially in the visible and near-infrared regions. Silver nanoparticles exhibit localized surface plasmon resonance (LSPR), which enhances the electromagnetic fields near the nanoparticle surface when exposed to light of specific wavelengths. This property can lead to:
Enhanced light absorption and scattering: Silver nanoparticles can increase the absorption of light in photocatalytic processes or fluorescence-based sensing applications by enhancing the local electric field near the nanoparticle surface.
In the CdS/Ag core-shell structure, the silver shell helps improve the stability, optical properties, and photocatalytic performance of the CdS core while minimizing the potential toxicity associated with the cadmium component.
- Synthesis of CdS/Ag Core-Shell Nanoparticles
The synthesis of CdS/Ag core-shell nanoparticles typically involves a two-step process:
Synthesis of CdS Core
The CdS core can be synthesized via several methods, such as colloidal synthesis or hydrothermal synthesis. In colloidal synthesis, cadmium precursors (like cadmium acetate or cadmium chloride) are reacted with sulfur sources (such as sodium sulfide or thiol compounds) in a solvent like oleylamine or octadecene. The size of the CdS nanoparticles can be controlled by adjusting the reaction temperature and the concentration of the precursors.
Deposition of Ag Shell
Once the CdS core is formed, the Ag shell can be deposited around the core using methods such as chemical reduction or electrochemical deposition. In chemical reduction, a silver salt (such as silver nitrate) is reduced in the presence of the CdS nanoparticles, forming a thin silver shell around the core. The thickness of the silver shell can be controlled by adjusting the precursor concentration and reaction time.
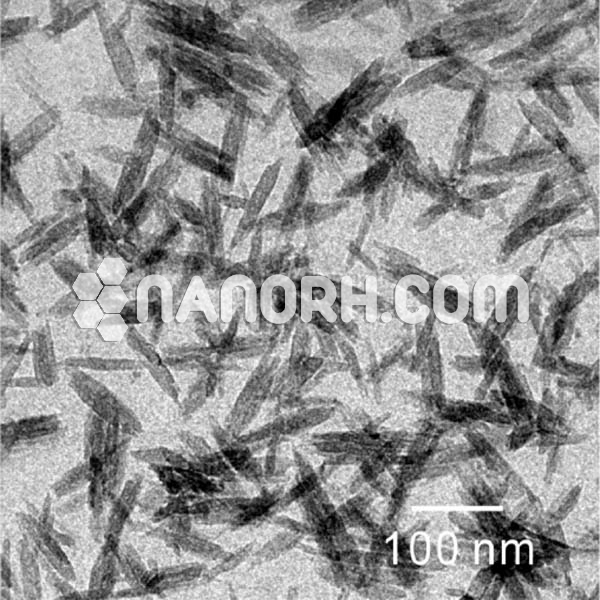
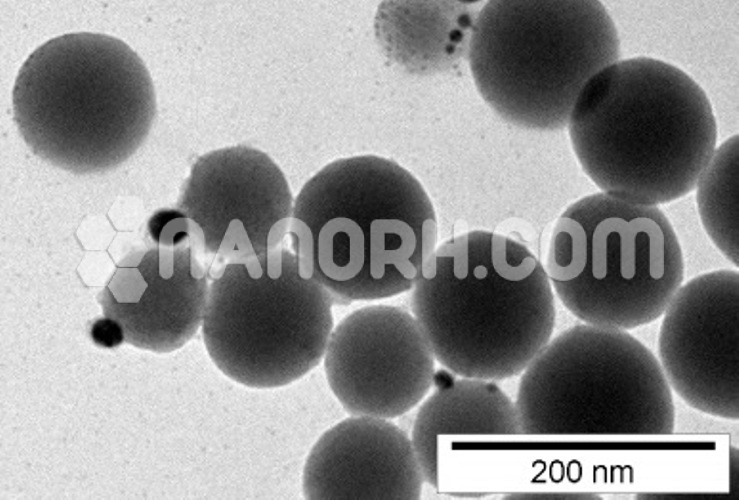
The resulting CdS/Ag core-shell nanoparticles can be characterized using a range of techniques, including scanning electron microscopy (SEM), transmission electron microscopy (TEM), X-ray diffraction (XRD), and UV-vis spectroscopy to assess their size, structure, optical properties, and crystallinity.