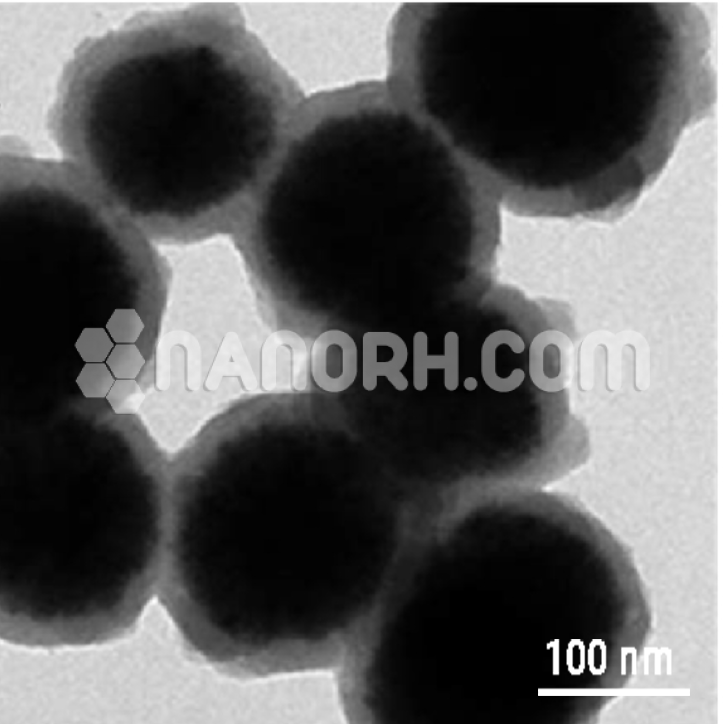
| Zinc Sulfide Manganese/ Zinc Oxide Core-Shell Nanoparticles | |
| Product No | NRE-16087 |
| CAS No. | 1314-98-3/1314-13-2 |
| Formula | ZnS: Mn/ZnO |
| APS | <100nm (can be customized) |
| Shape | Spherical |
| Purity | 99.9% |
| Core | Zinc Sulfide: Manganese |
| Shell | Zinc Oxide |
| Appearance | Powder |
| Boiling Point | NA |
Zinc Sulfide Manganese/ Zinc Oxide Core-Shell Nanoparticles
Biomedical Applications
Antibacterial and Antimicrobial Activity:
Zinc sulfide manganese/ zinc oxide core-shell nanoparticles and when used in the core of the core-shell structure, they contribute to antimicrobial activity through the generation of reactive oxygen species (ROS) under UV light exposure. The ZnO core is effective in killing bacteria, viruses, and fungi, making the nanoparticles useful in biomedical applications such as wound healing, medical device coatings, and infection prevention.
The ZnS
shell can also enhance the antibacterial effect through photocatalysis, especially when exposed to light, making these nanoparticles effective in self-cleaning surfaces and antibacterial coatings for implants, wound dressings, and surgical tools.
Drug Delivery and Controlled Release:
The biocompatibility of the ZnO core and ZnS
shell allows these nanoparticles to be employed in drug delivery applications. The ZnO core can be functionalized to carry drugs, and the ZnS
shell can be used to track the location and release of the drugs using fluorescence imaging.
These nanoparticles can be used for targeted drug delivery systems, where the drug payload is delivered specifically to the desired tissue or cell type, and the luminescent properties of the shell can be employed for tracking the release of drugs in real-time.
- Energy and Environmental Applications
Photocatalysis:
ZnO is a widely studied photocatalyst used for applications such as water splitting, pollutant degradation, and environmental cleanup. The ZnO core provides excellent photocatalytic properties when exposed to UV light, leading to the generation of electron-hole pairs that can drive oxidative reactions.
The ZnS
shell improves the overall photocatalytic efficiency by enhancing the charge separation and stability of the ZnO core, reducing the recombination of photogenerated electrons and holes. This leads to more efficient degradation of organic pollutants, water purification, and air cleaning applications.