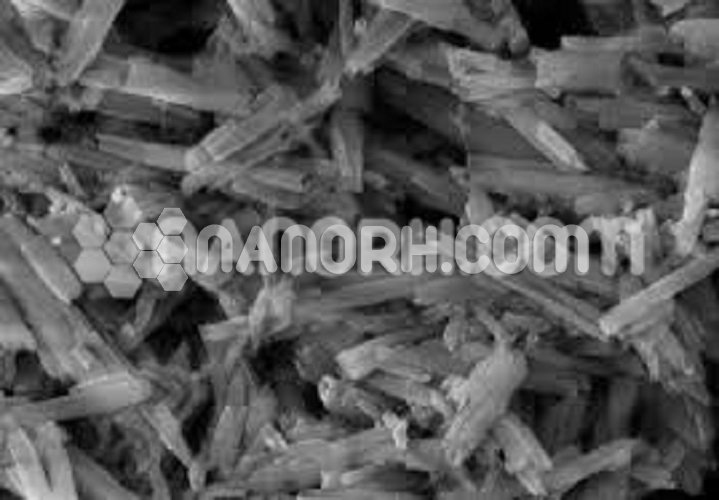
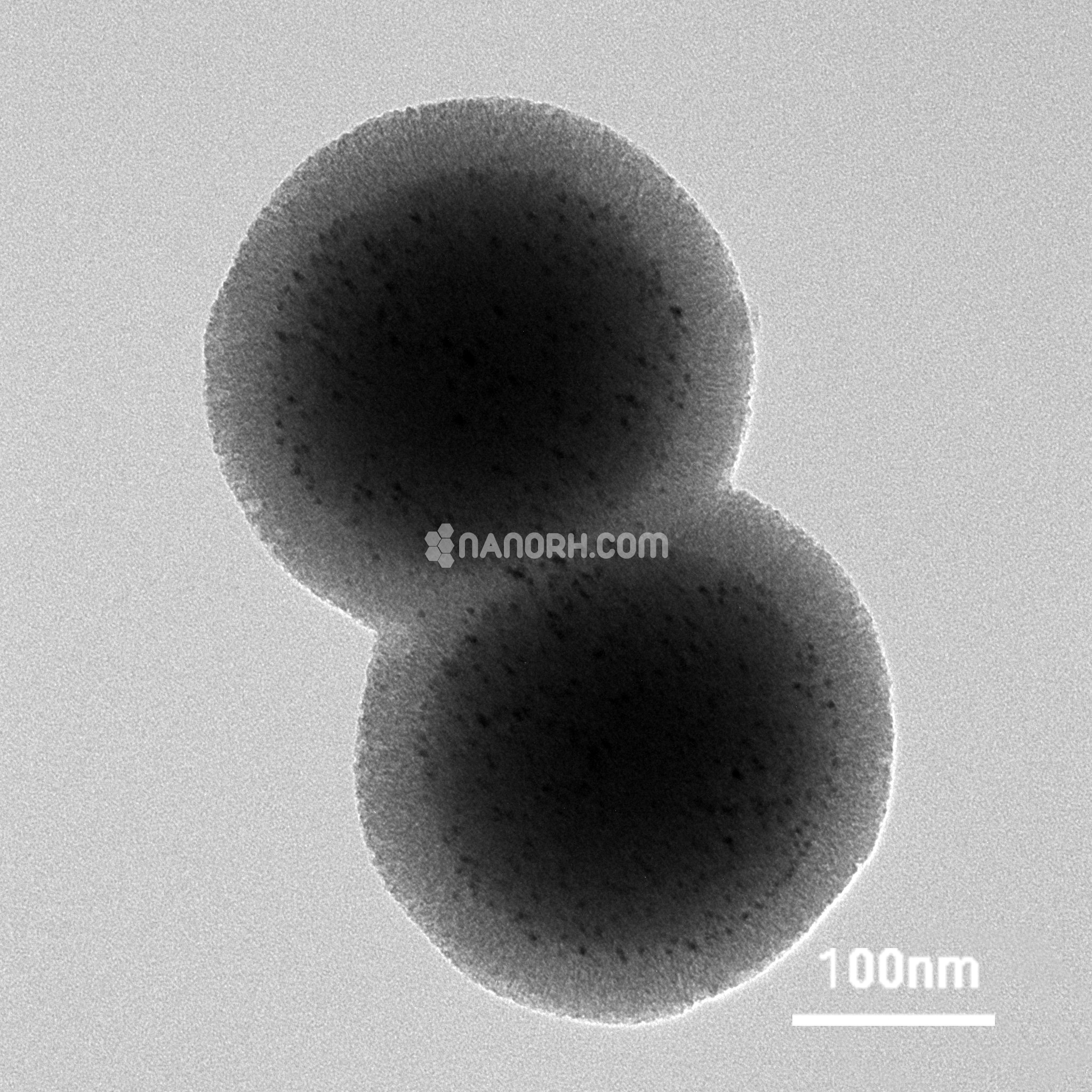
| Iron Platinum Core-Shell Nanoparticles | |
| Product No | NRE-16060 |
| CAS No. | 7440-48-4 |
| Formula | Fe/Pt |
| APS | <100nm (can be customized) |
| Shape | Spherical |
| Purity | 99.9% |
| Core | Iron |
| Shell | Platinum |
| Appearance | Powder |
| Boiling Point | NA |
Iron Platinum Core-Shell Nanoparticles
Introduction
Introduction
Iron Platinum (FePt) core-shell nanoparticles are a class of composite nanomaterials that combine the properties of iron (Fe) and platinum (Pt). In this core-shell structure, the Fe core provides strong magnetic properties, while the Pt shell imparts high chemical stability, catalytic activity, and electronic functionality. The unique combination of these materials makes FePt core-shell nanoparticles versatile for a range of applications, including magnetic storage, catalysis, biomedical imaging, and drug delivery.
Iron (Fe) Core: The iron core typically consists of Fe₃O₄ (magnetite) or Fe₇₆Pt₂₄ alloys. The core contributes magnetic properties, such as superparamagnetism, which allows the nanoparticles to be manipulated by external magnetic fields without retaining magnetization after the field is removed. This makes them ideal for magnetic targeting and separation applications.
Platinum (Pt) Shell: Platinum is known for its high chemical stability and catalytic properties. The platinum shell in FePt nanoparticles enhances corrosion resistance, providing durability in harsh environments. Additionally, platinum imparts catalytic activity for reactions like hydrogenation or fuel cell reactions, making these nanoparticles useful in green energy and environmental applications.
The core-shell architecture optimizes the properties of both materials, enabling these nanoparticles to combine the magnetic advantages of Fe with the chemical and catalytic properties of Pt, all within a single structure.
Properties of FePt Core-Shell Nanoparticles
Magnetic Properties (Fe Core)
Superparamagnetism: The iron core provides superparamagnetism, where nanoparticles can be magnetized in the presence of an external magnetic field but lose their magnetization once the field is removed. This property allows for easy manipulation and control of the nanoparticles, especially in biomedical applications (e.g., drug delivery, magnetic resonance imaging).
High Magnetic Anisotropy: The iron core imparts high magnetic stability to the nanoparticles. This makes them ideal for applications where high thermal stability and robust magnetic performance are required.
Catalytic Properties (Pt Shell)
High Catalytic Activity: The platinum shell gives FePt core-shell nanoparticles excellent catalytic properties, particularly in hydrogenation, fuel cell reactions, and green chemistry. Platinum is one of the most active metals for catalysis, and the Pt shell allows these nanoparticles to act as efficient catalysts without suffering from corrosion.